The world’s most popular programming language just got a new update.
Ever since 2015, a new JavaScript version has come out every year with tons of powerful features to make life much easier, and 2023 has been no different. Let’s look at what ES14 has to offer.
1. Array toSorted() method
Sweet syntactic sugar.
ES14 comes with a new toSorted() method that makes it easier to sort an array and return a copy without mutation.
So instead of doing this:
const nums = [5, 2, 6, 3, 1, 7, 4];
const clone = [...nums];
const sorted = clone.sort();
console.log(sorted); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
We now get to do this:
const nums = [5, 2, 6, 3, 1, 7, 4];
const sorted = nums.toSorted();
console.log(sorted); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
console.log(nums); // [5, 2, 6, 3, 1, 7, 4]
And just like sort(), toSorted() takes a callback function that lets you decide how the sort should happen – ascending or descending, alphabetical or numeric.
const nums = [5, 2, 6, 3, 1, 7, 4];
const sorted = nums.toSorted((a, b) => b - a);
console.log(sorted); // [7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
2. Hashbang grammar
What’s a hashbang?
Basically, it’s a sequence of characters in a file that tells the Linux Shell what interpreter or engine it should use to run the file. For example:
#!/bin/bash
echo "How are you all doing today?"
With this hashbang, we can now easily run codingbeauty.sh directly in the shell, after using the chmod command to make the script executable.
Hashbangs also let us hide all the juicy implementation details in our scripts and indicate specific interpreter versions to execute the script files.
So with ES14, we can now do this effortlessly in JavaScript files, like this:
#!/usr/bin/env node
console.log("I'm doing great, how are you?");
3. Array toSpliced() method
Those immutability purists out there will no doubt be pleased with all these new Array methods.
toSorted() is to sort() as toSpliced() is to splice():
const colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'pink'];
const spliced = colors.toSpliced(1, 2, 'gray', 'white');
console.log(spliced); // [ 'red', 'gray', 'white', 'yellow', 'pink' ]
// Original not modified
console.log(colors); // ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'pink'];
Here toSpliced() removes 2 of the array elements, starting from index 1, and inserts 'gray' and 'white' in their place.
4. Symbols as WeakMap keys
WeakMaps; not very popular, are they?
Well, they’re a lot like Maps, except their keys can only contain non-primitive objects – no strings or numbers allowed here. These keys are stored as weak references, meaning the JavaScript engine can carry out garbage collection on the objects when it needs to if there is no other reference to the objects in memory apart from the keys.
One powerful use of WeakMaps is custom caching: by using objects as keys, you can associate cached values with specific objects. When the objects are garbage collected, the corresponding WeakMap entries are automatically removed, clearing the cache immediately.
const map = new Map();
const weakMap = new WeakMap();
const obj1 = { name: 'React' };
const obj2 = { name: 'Angular' };
map.set(obj1, 'Value for obj1 at Coding Beauty');
weakMap.set(obj2, 'Value for obj2 at Coding Beauty');
console.log(map.get(obj1)); // Output: Value for obj1
console.log(weakMap.get(obj2)); // Output: Value for obj2
obj1 = null;
obj2 = null;
console.log(map.get(obj1)); // Output: Value for obj1
console.log(weakMap.get(obj2)); // Output: undefined (obj2 has been garbage collected)
So ES14 makes it possible to define JavaScript Symbols as keys. This can make the role a key-value pair plays in a WeakMap clearer.
let mySymbol = Symbol('mySymbol');
let myWeakMap = new WeakMap();
let obj = {
name: 'Coding Beauty'
};
myWeakMap.set(mySymbol, obj);
console.log(myWeakMap.get(mySymbol)); // Output: object
And what are they meant for?
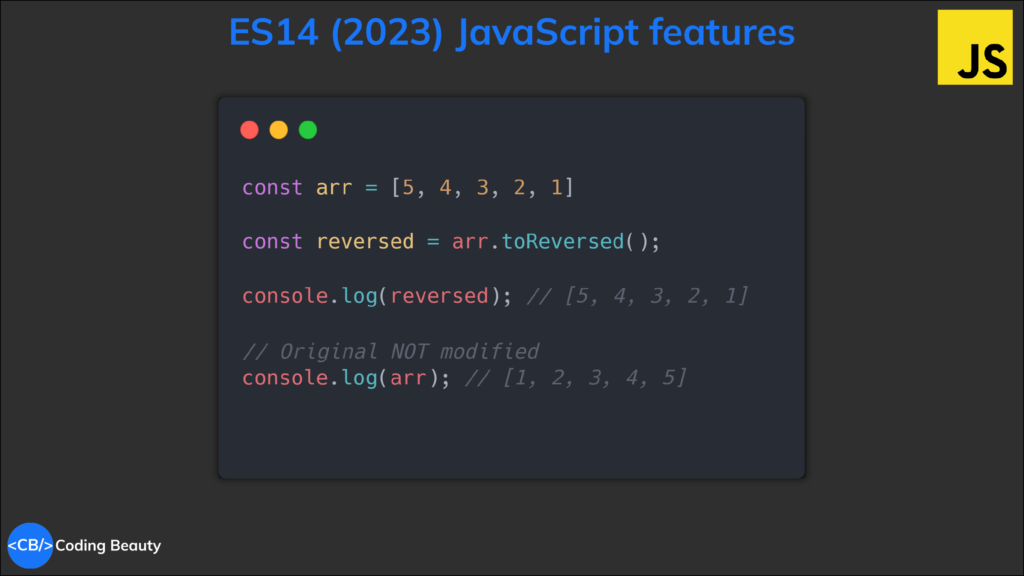
5. Array toReversed() method
Another new Array method to promote immutability and functional programming.
The name’s self-explanatory: give me the reversed version of my array.
Before – with reverse().
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
const reversed = arr.reverse();
console.log(reversed); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// Original modified
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Now:
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
const reversed = arr.toReversed();
console.log(reversed); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
// Original NOT modified
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
6. Array find from last
Sure we can already use the Array find() method to find an element in an array that passes a specified test condition. And findIndex() will give us the index of such an element.
But find() and findIndex() both start searching from the first element of the array. What if it’ll be better for us to search from the last element instead?
Here we’re trying to get the item in the array with the value prop equal to y. With find() and findIndex():
const letters = [
{ value: 'v' },
{ value: 'w' },
{ value: 'x' },
{ value: 'y' },
{ value: 'z' },
];
const found = letters.find((item) => item.value === 'y');
const foundIndex = letters.findIndex((item) => item.value === 'y');
console.log(found); // { value: 'y' }
console.log(foundIndex); // 3
This works, but as the target object is closer to the tail of the array, we could make this program run faster if we use the new ES2022 findLast() and findLastIndex() methods to search the array from the end.
const letters = [
{ value: 'v' },
{ value: 'w' },
{ value: 'x' },
{ value: 'y' },
{ value: 'z' },
];
const found = letters.findLast((item) => item.value === 'y');
const foundIndex = letters.findLastIndex((item) => item.value === 'y');
console.log(found); // { value: 'y' }
console.log(foundIndex); // 3
Another use case might require that we specifically search the array from the end to get the correct item. For example, if we want to find the last even number in a list of numbers, find() and findIndex() would produce a totally wrong result.
const nums = [7, 14, 3, 8, 10, 9];
// gives 14, instead of 10
const lastEven = nums.find((value) => value % 2 === 0);
// gives 1, instead of 4
const lastEvenIndex = nums.findIndex((value) => value % 2 === 0);
console.log(lastEven); // 14
console.log(lastEvenIndex); // 1
Yes, we could call the reverse() method on the array to reverse the order of the elements before calling find() and findIndex().
But this approach would cause unnecessary mutation of the array, as reverse() reverses the elements of an array in place. The only way to avoid this mutation would be to make a new copy of the entire array, which could cause performance problems for large arrays.
And this beside the fact that findIndex() would still not work on the reversed array, as reversing the elements would also mean changing the indexes they had in the original array. To get the original index, we would need to perform an additional calculation, which means writing more code.
const nums = [7, 14, 3, 8, 10, 9];
// Copying the entire array with the spread syntax before
// calling reverse()
const reversed = [...nums].reverse();
// correctly gives 10
const lastEven = reversed.find((value) => value % 2 === 0);
// gives 1, instead of 4
const reversedIndex = reversed.findIndex((value) => value % 2 === 0);
// Need to re-calculate to get original index
const lastEvenIndex = reversed.length - 1 - reversedIndex;
console.log(lastEven); // 10
console.log(reversedIndex); // 1
console.log(lastEvenIndex); // 4
It’s in cases like where the findLast() and findLastIndex() methods come in handy.
const nums = [7, 14, 3, 8, 10, 9];
const lastEven = nums.findLast((num) => num % 2 === 0);
const lastEvenIndex = nums.findLastIndex((num) => num % 2 === 0);
console.log(lastEven); // 10
console.log(lastEvenIndex); // 4
This code is shorter and more readable. Most importantly, it produces the correct result.
7. Array with() method
Unlike the others, with() has no complementary mutating method. But once you see it in action, you’ll know that it’s the immutable approach to changing a single element.
In so many languages, you typically modify a single array element like this:
const arr = [5, 4, 7, 2, 1]
// Mutates array to change element
arr[2] = 3;
console.log(arr); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
But see what we can do now, in ES2023 JavaScript:
const arr = [5, 4, 7, 2, 1];
const replaced = arr.with(2, 3);
console.log(replaced); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
// Original not modified
console.log(arr); // [5, 4, 7, 2, 1]
Final thoughts
This year was all about easier functional programming and immutability.
Indeed, the reliability and consistency that immutability brings cannot be overstated. With the rise of declarative frameworks like React and Vue as well as Redux and other libraries, we’ve seen immutable JavaScript array methods explode in popularity; it’s only natural that we see more and more of them come baked into the language as it matures.
They stole the show in 2023, just like JavaScript took over a huge chunk of the language ecosystem a while back, with many millions of developers keeping that fire burning today. Let’s see what the future holds.