Related: How to Get an Input Field’s Value in React
To get the value of an input field on button click in React:
- Create a state variable to store the value of the input field.
- Set an
onChangeevent handler on the input to update the state variable when the input field value changes. - Set an
onClickevent handler on a button element. - Access the state variable in the event handler.
For example:
App.js
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function App() {
const [message, setMessage] = useState('');
const [updated, setUpdated] = useState(message);
const handleChange = (event) => {
setMessage(event.target.value);
};
const handleClick = () => {
// 👇 "message" stores input field value
setUpdated(message);
};
return (
<div>
<input
type="text"
id="message"
name="message"
onChange={handleChange}
value={message}
/>
<h2>Message: {message}</h2>
<h2>Updated: {updated}</h2>
<button onClick={handleClick}>Update</button>
</div>
);
}
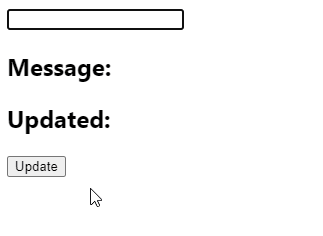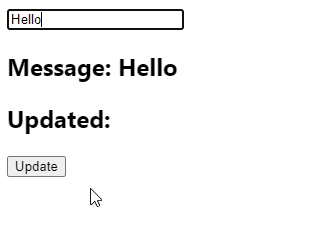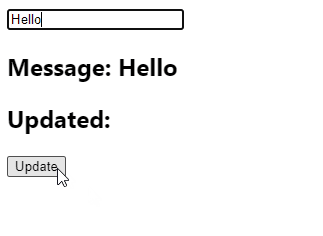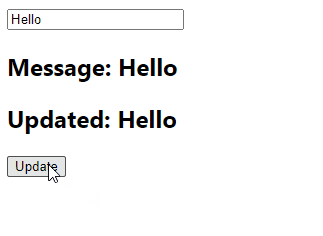
With the useState() hook we create a state variable (message) to store the current value of the input field. We also create another state variable (updated) that will be updated with the input field value when the button is clicked.
We set an onChange event handler on the input field to make this handler get called whenever the input value changes. In the handler, we use the event.target property to access the object representing the input element. The value property of this object contains the input value, so we pass it to setMessage() to update message, and this reflects on the page.
After setting up the controlled input, we can now use message outside the handleChange handler to access the current value of the input field.
So in the onClick event handler we set on the button, we use setUpdated(message) to update the updated variable with the current input field value.
Get value of uncontrolled input on button click
To get the value of an uncontrolled input on button click in React:
- Create a ref for the input field
- Set an
onClickevent handler on thebutton. - Use the ref object to access the current input value in the event handler.
For example:
App.js
import { useRef, useState } from 'react';
export default function App() {
const inputRef = useRef(null);
const [updated, setUpdated] = useState('');
const handleClick = () => {
// 👇 "inputRef.current.value" is input value
setUpdated(inputRef.current.value);
};
return (
<div>
<input
ref={inputRef}
type="text"
id="message"
name="message"
/>
<h2>Updated: {updated}</h2>
<button onClick={handleClick}>Update</button>
</div>
);
}
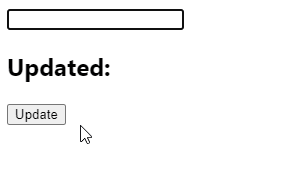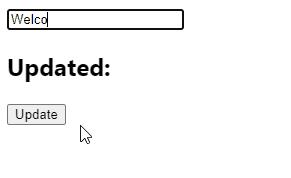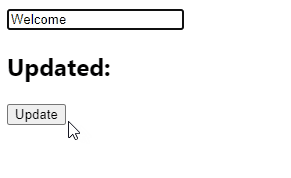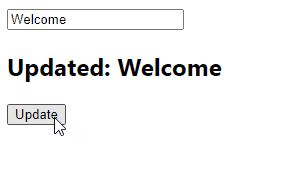
While the data in a controlled input is handled by React state, the data in an uncontrolled input is handled by the DOM itself. This is why the input in the example above doesn’t have a value prop or onChange event handler set. Instead, we access the input field value with a React ref. The DOM updates this value when the text in the input is changed.
We create a ref object with the useRef() hook and set it to the ref prop of the input. Doing this sets the current property of the ref object to the DOM object that represents the input element.
useRef() returns a mutable ref object that does not change value when a component is updated. Also, modifying the value of this object’s current property does not cause a re-render. This is in contrast to the setState update function returned from useState().
Although the React documentation recommends using controlled components, uncontrolled components offer some advantages. You might prefer them if the form is very simple and doesn’t need instant validation, and values only need to be accessed when the form is submitted.
Every Crazy Thing JavaScript Does
A captivating guide to the subtle caveats and lesser-known parts of JavaScript.

Thank you so much for this idea.
love from india 🙂