We use the current URL in a web app to track user activity, maintain history, or modify displayed elements based on route. So, let’s see how to quickly get the current URL in a Next.js app.
In this article
- Get current URL in Next.js Pages Router component
- Get current URL in Next.js App Router component
- Get current URL in Next.js getServerSideProps
Get current URL in Next.js Pages Router component
To get the current URL in a Next.js component, use the useUrl hook from the nextjs-current-url package:
With pages directory:
import { useUrl } from 'nextjs-current-url';
import Head from 'next/head';
export default function Home() {
const { href: currentUrl, pathname } = useUrl() ?? {};
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>Next.js - Coding Beauty</title>
<meta name="description" content="Next.js Tutorials by Coding Beauty" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<link rel="icon" href="/favicon.png" />
</Head>
<main>
Welcome to Coding Beauty 😄
<br />
<br />
URL: <b>{currentUrl}</b>
<br />
pathname: <b>{pathname}</b>
</main>
</>
);
}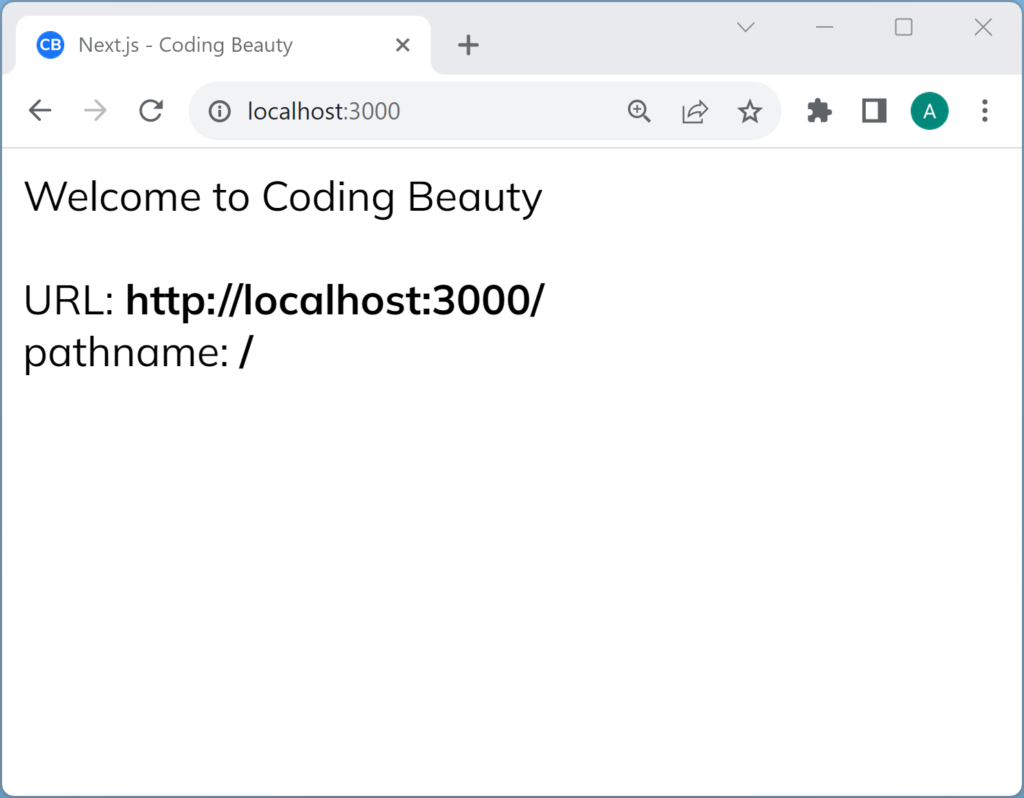
useUrl() returns a URL object that gives us more info on the current URL.
Get current URL with useState and window.location.href
We can also get the current URL in a client component using useState and window.location.href.
import Head from 'next/head';
import { useRouter } from 'next/router';
import { useEffect } from 'react';
export default function Home() {
const [currentUrl, setCurrentUrl] = useState<string | null>(null);
const { pathname } = useRouter();
useEffect(() => {
setCurrentUrl(window.location.href);
}, []);
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>Next.js - Coding Beauty</title>
<meta name="description" content="Next.js Tutorials by Coding Beauty" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<link rel="icon" href="/favicon.ico" />
</Head>
<main>
Welcome to Coding Beauty 😄
<br />
<br />
URL: <b>{currentUrl}</b>
<br />
pathname: <b>{pathname}</b>
</main>
</>
);
}The window.location.href property returns a string containing the entire page URL, and we use the useState and useEffect hooks to create and set state for storing the current URL.
window.location property
window.location has other properties that tell you more about the URL. Like:
pathname: the path of theURLafter the domain name and any optional port number. Query and fragment identifier not included.protocol:URL‘s protocol scheme, likehttps:ormailto:. Doesn’t include the//.hostname: theURL‘s domain name without the port number.
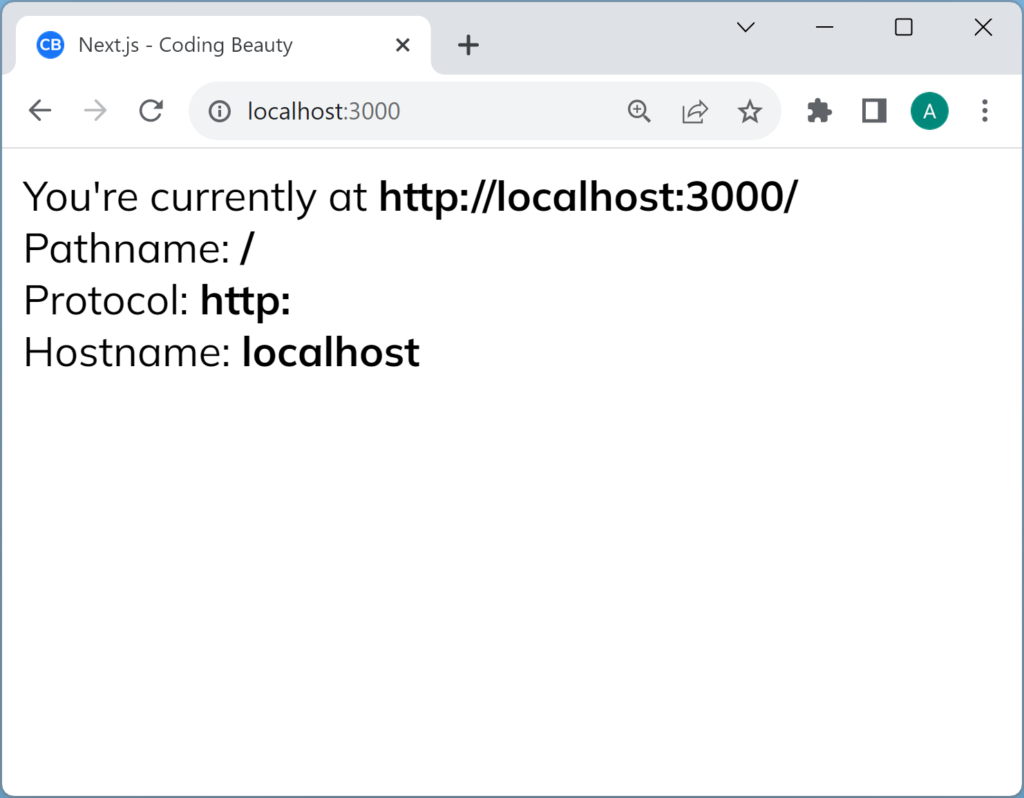
Here’s an example where we use some of these properties:
import { getUrl } from '@/lib/utils/get-url';
import { NextPageContext } from 'next';
import Head from 'next/head';
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
export function getServerSideProps(context: NextPageContext) {
return {
props: {
currentUrl: getUrl({ req: context.req! })?.href,
},
};
}
export default function Home() {
const [myLocation, setMyLocation] = useState<Location | null>(null);
useEffect(() => {
setMyLocation(window.location);
});
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>Next.js - Coding Beauty</title>
<meta name="description" content="Next.js Tutorials by Coding Beauty" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<link rel="icon" href="/favicon.png" />
</Head>
<main>
You are currently accessing <b>{myLocation?.href}</b> 😃
<br />
Pathname: <b>{myLocation?.pathname}</b>
<br />
Protocol: <b>{myLocation?.protocol}</b>
<br />
Hostname: <b>{myLocation?.hostname}</b>
</main>
</>
);
}
We need useEffect to get the current URL
Pages render on both the server and client in Next.js, so when the server renders the page, there’s no window object available.
So you’ll get a “window is not defined” error if you try to use window before hydration:
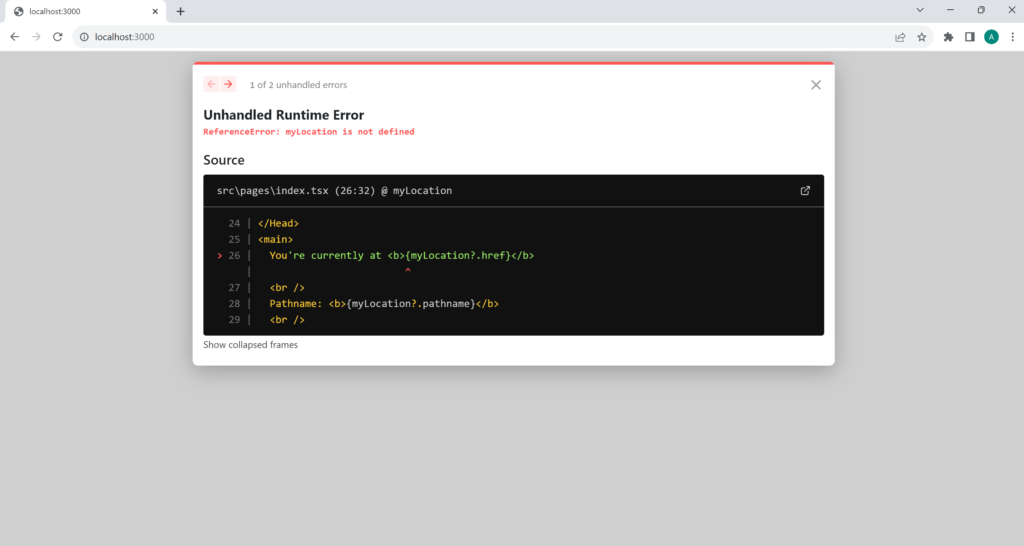
That’s why we use useEffect – to wait till mounting/hydration is done.
What’s hydration?
Hydration is when a server-generated web page gets extra client-side features added by the user’s web browser. Features like event listeners, client-side routing, etc.
Get current URL in Next.js App Router component
To get the current URL in a Next.js app router component, we can also use the useUrl hook from the nextjs-current-url library.
'use client';
import React from 'react';
import { useUrl } from 'nextjs-current-url';
import { Metadata } from 'next';
export const metadata: Metadata = {
title: 'Next.js - Coding Beauty',
description: 'Next.js Tutorials by Coding Beauty',
};
export default function Page() {
const { pathname, href } = useUrl() ?? {};
return (
<main>
Welcome to Coding Beauty
<br />
<br />
URL: <b>{href}</b>
<br />
route: <b>{pathname}</b>
</main>
);
}
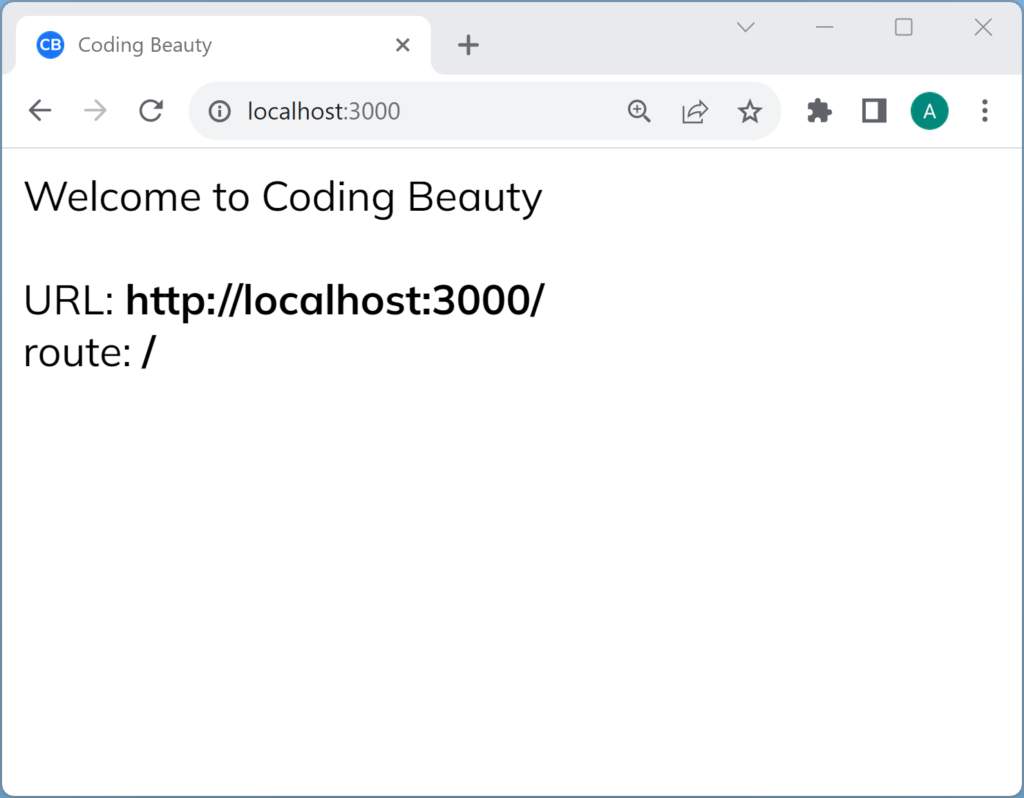
Next.js App Router: We need 'use client'
Notice the 'use client' statement at the top.
It’s there because all components in the new app directory are server components by default, so we can’t use any client-side specific APIS.
We’ll get an error if we try to do anything interactive with useEffect or other hooks like useUrl, because it’s a server environment.
Get current URL in Next.js getServerSideProps
To get the current URL in getServerSideProps of a Next.js page, use the getUrl function from the nextjs-current-url library.
import { NextPageContext } from 'next';
import Head from 'next/head';
import { getUrl } from 'nextjs-current-url/server';
export function getServerSideProps(context: NextPageContext) {
const url = getUrl({ req: context.req });
return {
props: {
url: url.href,
},
};
}
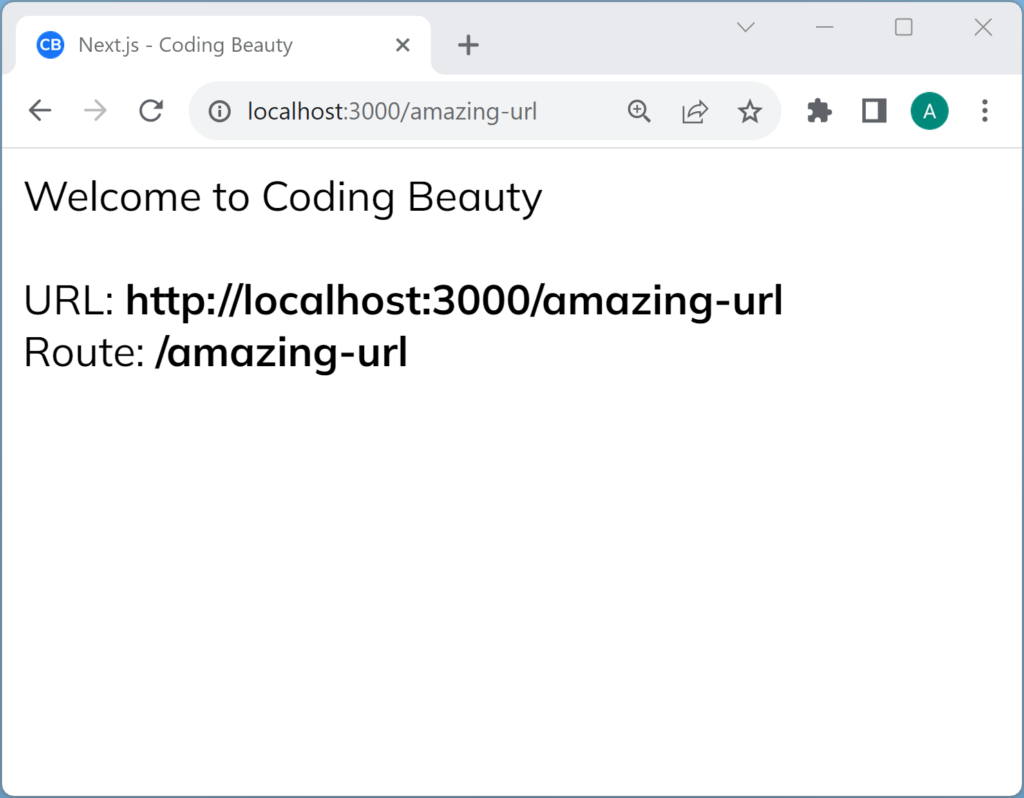
export default function Home({ url }: { url: string }) {
const urlObj = new URL(url);
const { pathname } = urlObj;
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>Next.js - Coding Beauty</title>
<meta name="description" content="Generated by create next app" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<link rel="icon" href="/favicon.png" />
</Head>
<main>
Welcome to Coding Beauty 😃
<br />
<br />
URL: <b>{url}</b>
<br />
Route: <b>{pathname}</b>
</main>
</>
);
}
Let’s check out some more properties of URL:
import { NextPageContext } from 'next';
import Head from 'next/head';
import { getUrl } from 'nextjs-current-url/server';
export function getServerSideProps(context: NextPageContext) {
const url = getUrl({ req: context.req });
return {
props: {
url: url.href,
},
};
}
export default function Home({ url }: { url: string }) {
const urlObj = new URL(url);
const { pathname, href, protocol, hostname, search, hash } = urlObj;
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>Next.js - Coding Beauty</title>
<meta name="description" content="Generated by create next app" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<link rel="icon" href="/favicon.png" />
</Head>
<main>
Welcome to Coding Beauty 😃
<br />
<br />
URL: <b>{href}</b>
<br />
Pathname: <b>{pathname}</b>
<br />
Protocol: <b>{protocol}</b>
<br />
Hostname: <b>{hostname}</b>
<br />
Search: <b>{search}</b>
<br />
Hash: <b>{hash}</b>
</main>
</>
);
}Here’s what these properties do:
href: the complete URL, including the protocol, hostname, port number, path, query parameters, and fragment identifier.protocol:URL’s protocol scheme, likehttps:ormailto:. Doesn’t include the//.hostname: the URL’s domain name without the port number.pathname: the URL’s path and filename without the query and fragment identifier.search: the URL’s query parameters. Includes the?hash: the fragment identifier, the part after the#.
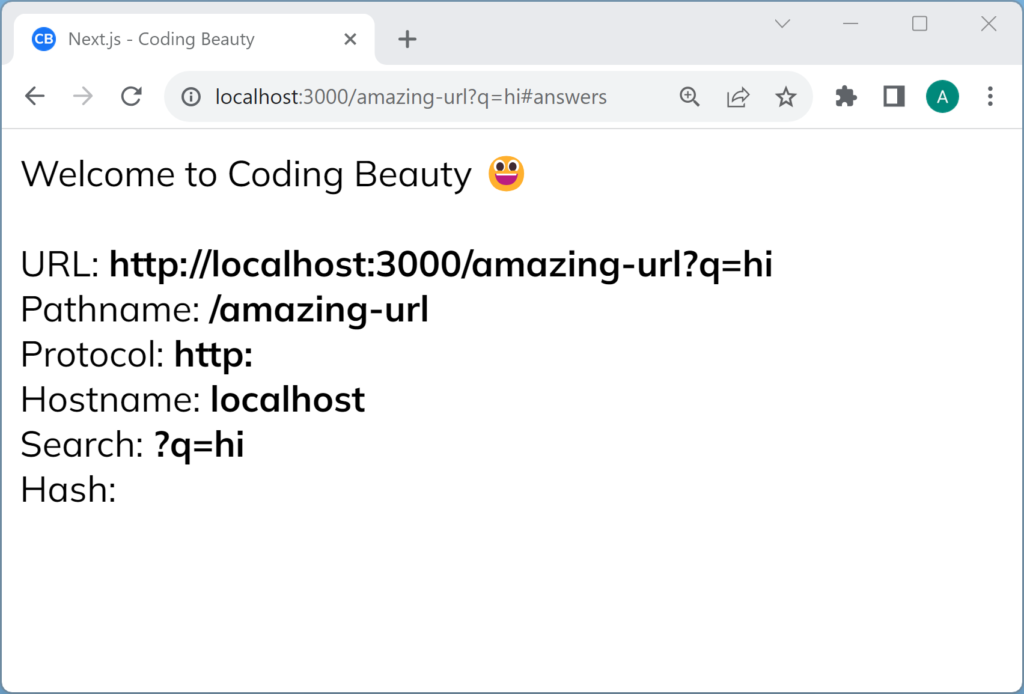
Note: As you can see it’s not possible to get the hash/fragment in getServerSideProps because the browser never sends the part after the # to the server. That’s why there’s no hash here. We’d have to get the current URL in the client-side to access the fragment identifier.
Every Crazy Thing JavaScript Does
A captivating guide to the subtle caveats and lesser-known parts of JavaScript.