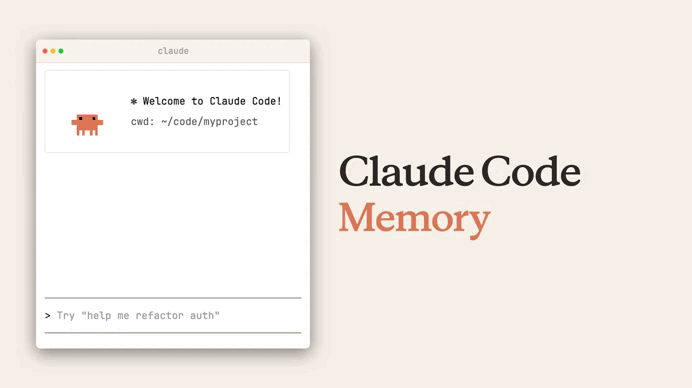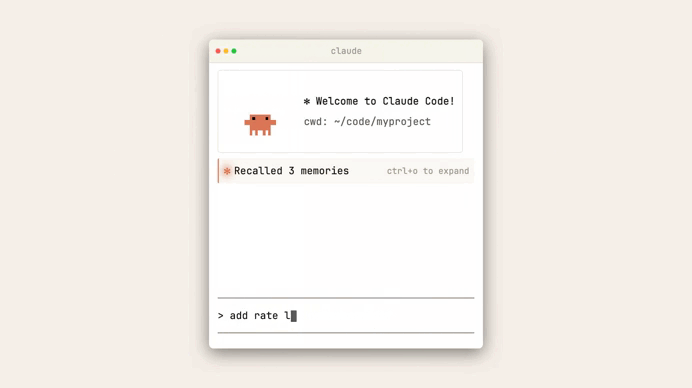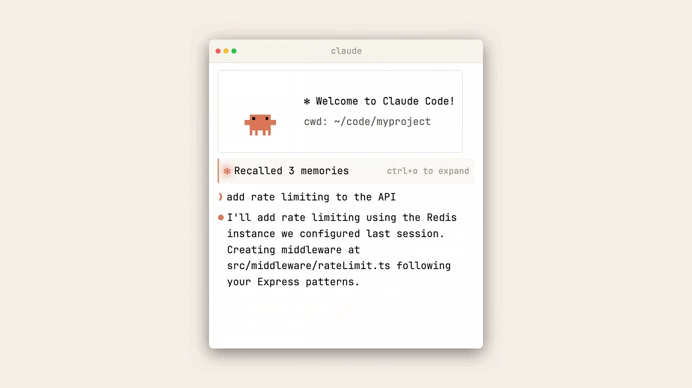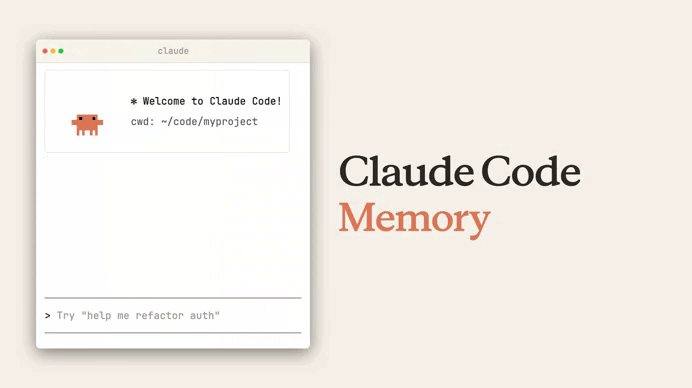
Claude Code’s new AI code review feature is simply unbelievable
Wow this is just too good. Anthropic just won’t stop releasing new game-changing features.
Now we just got a brilliant new Code Review feature in Claude Code — a much much needed addition in this grand modern era of AI-assisted coding.
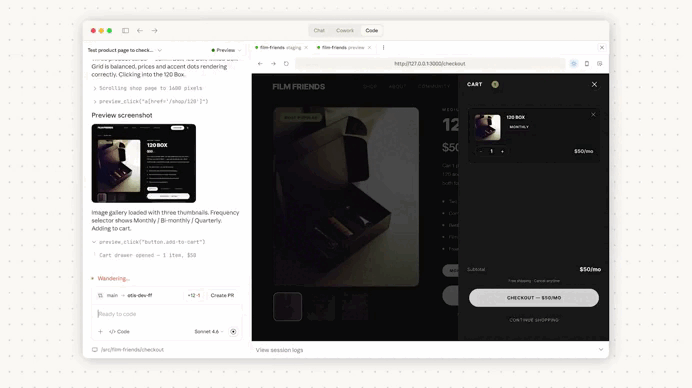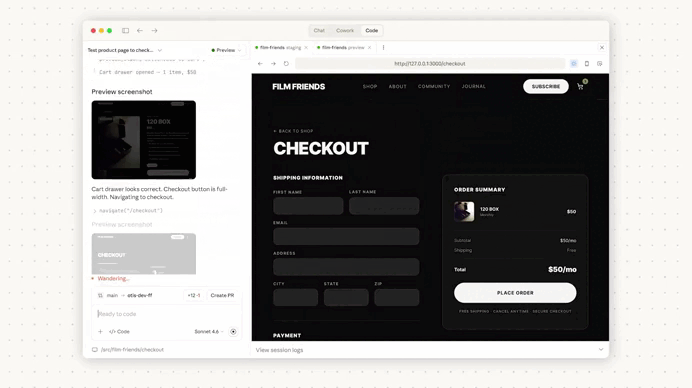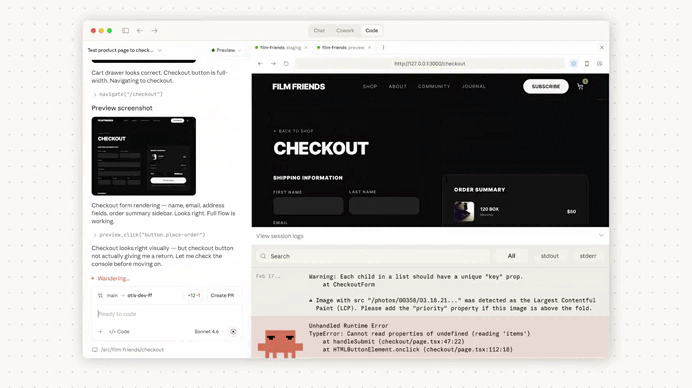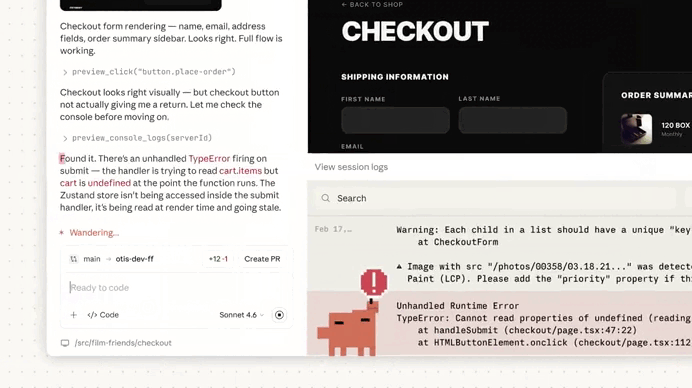
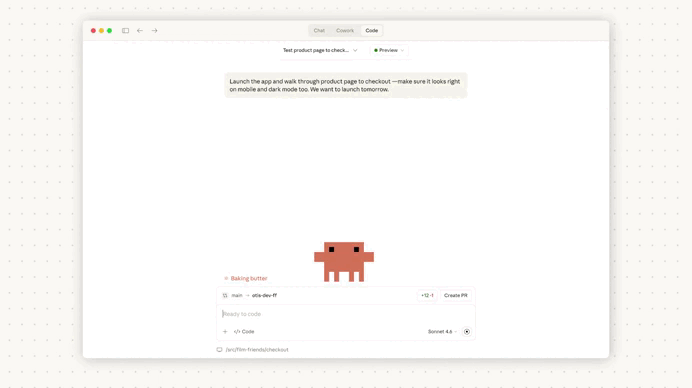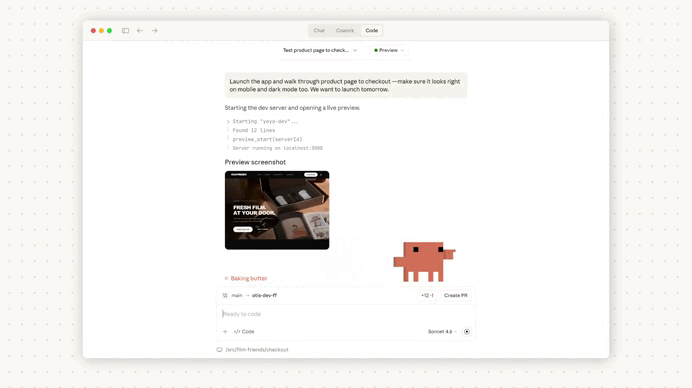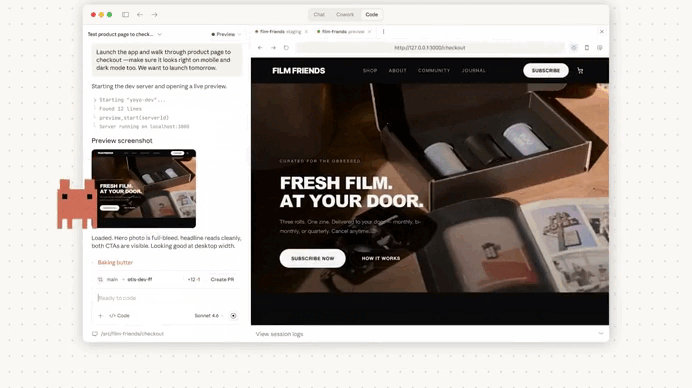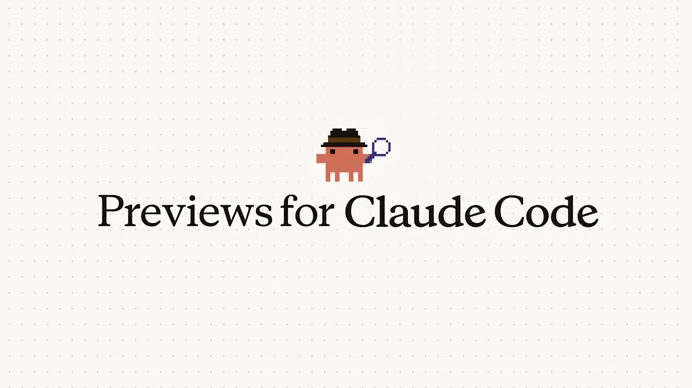
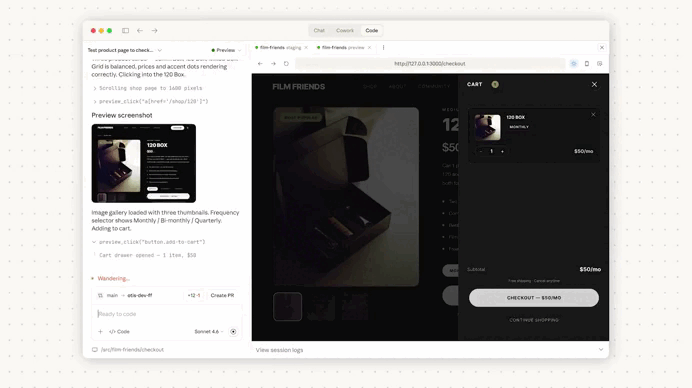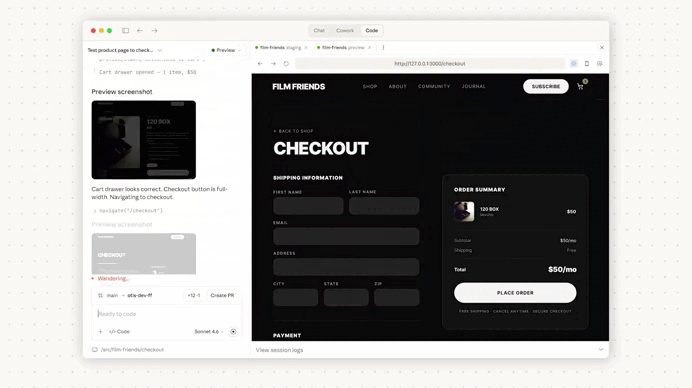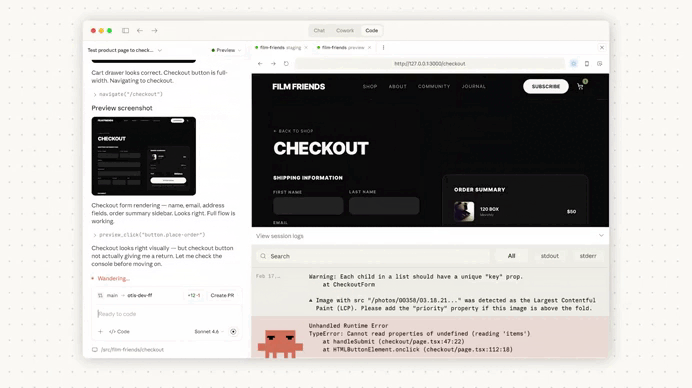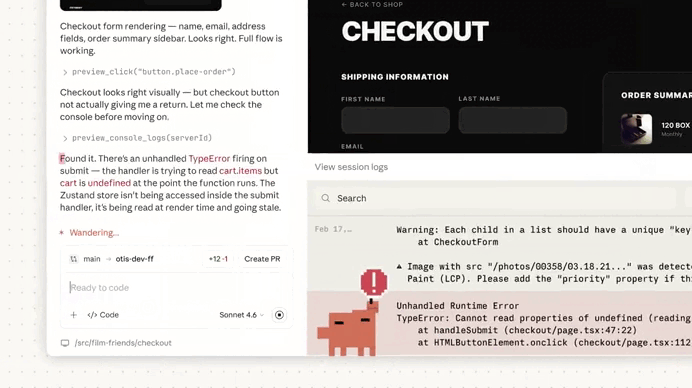
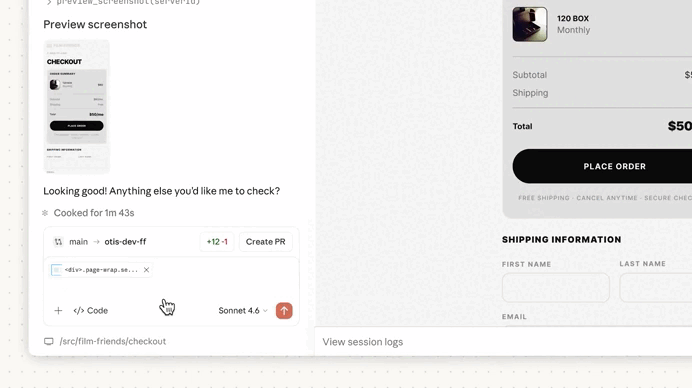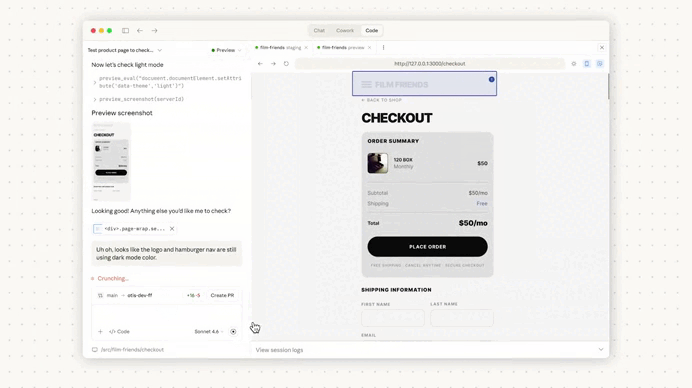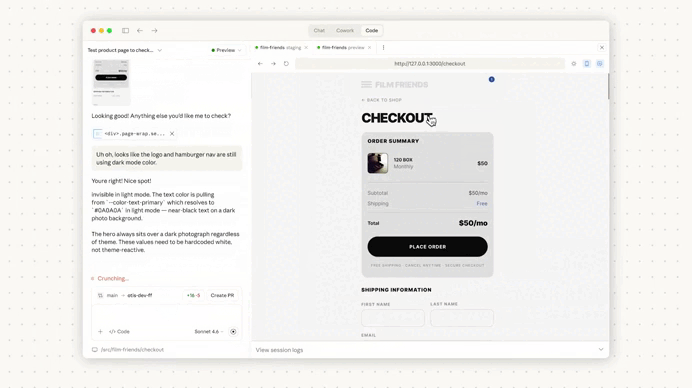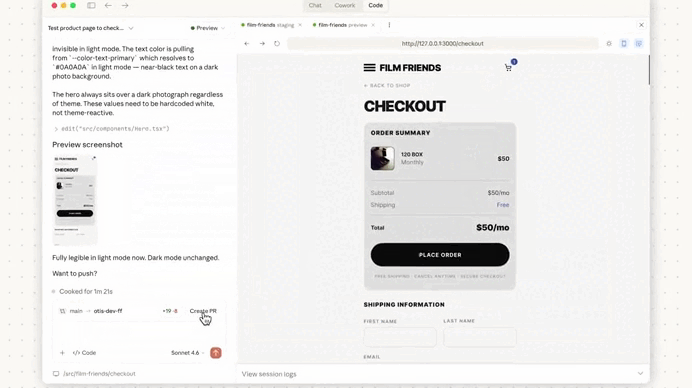
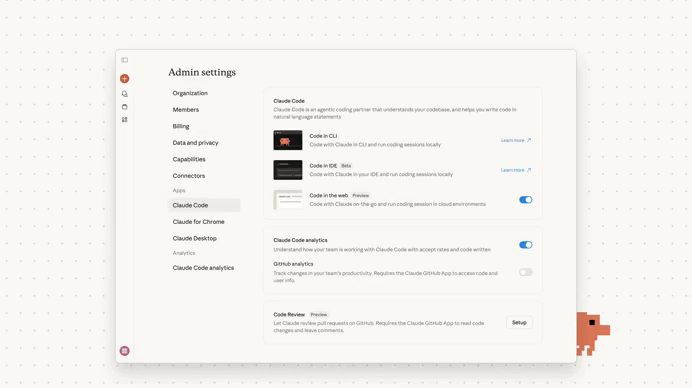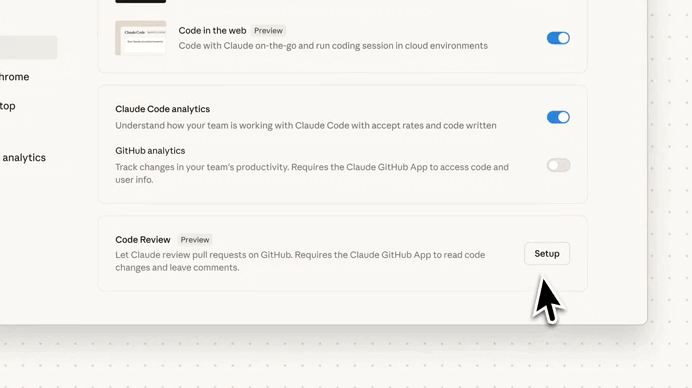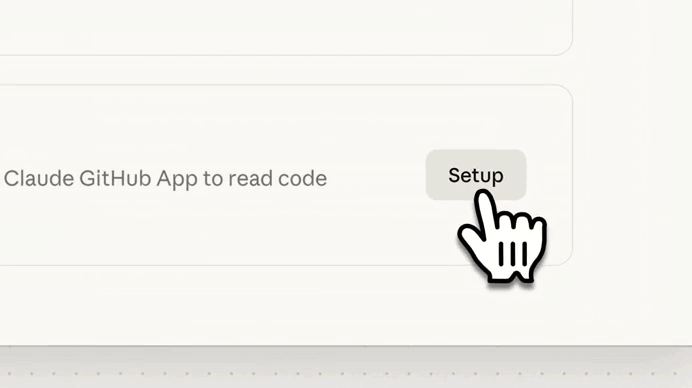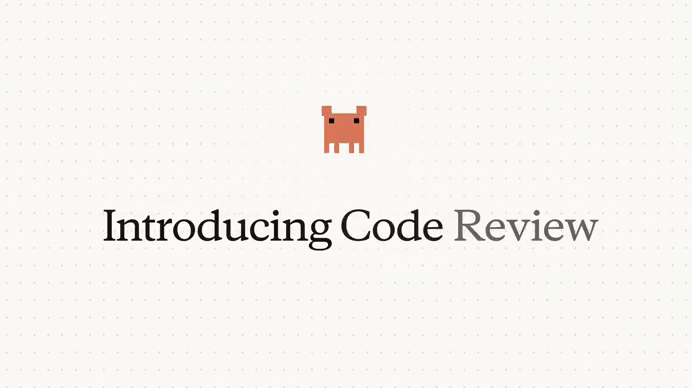
Just look at how amazing it was in action — first we set it up in Claude Code:
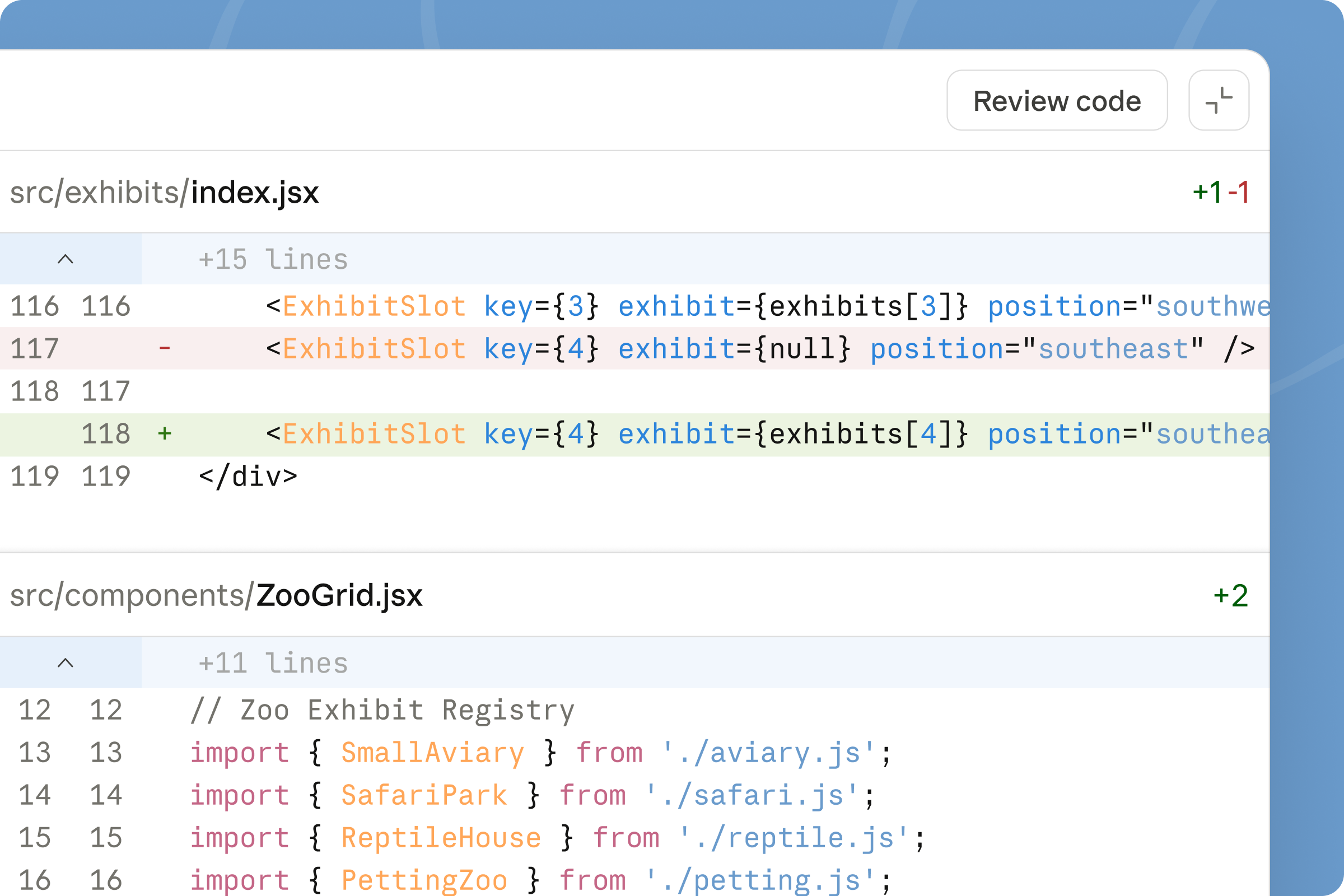
We used Claude Code to make a change to the codebase — this is the coding part:

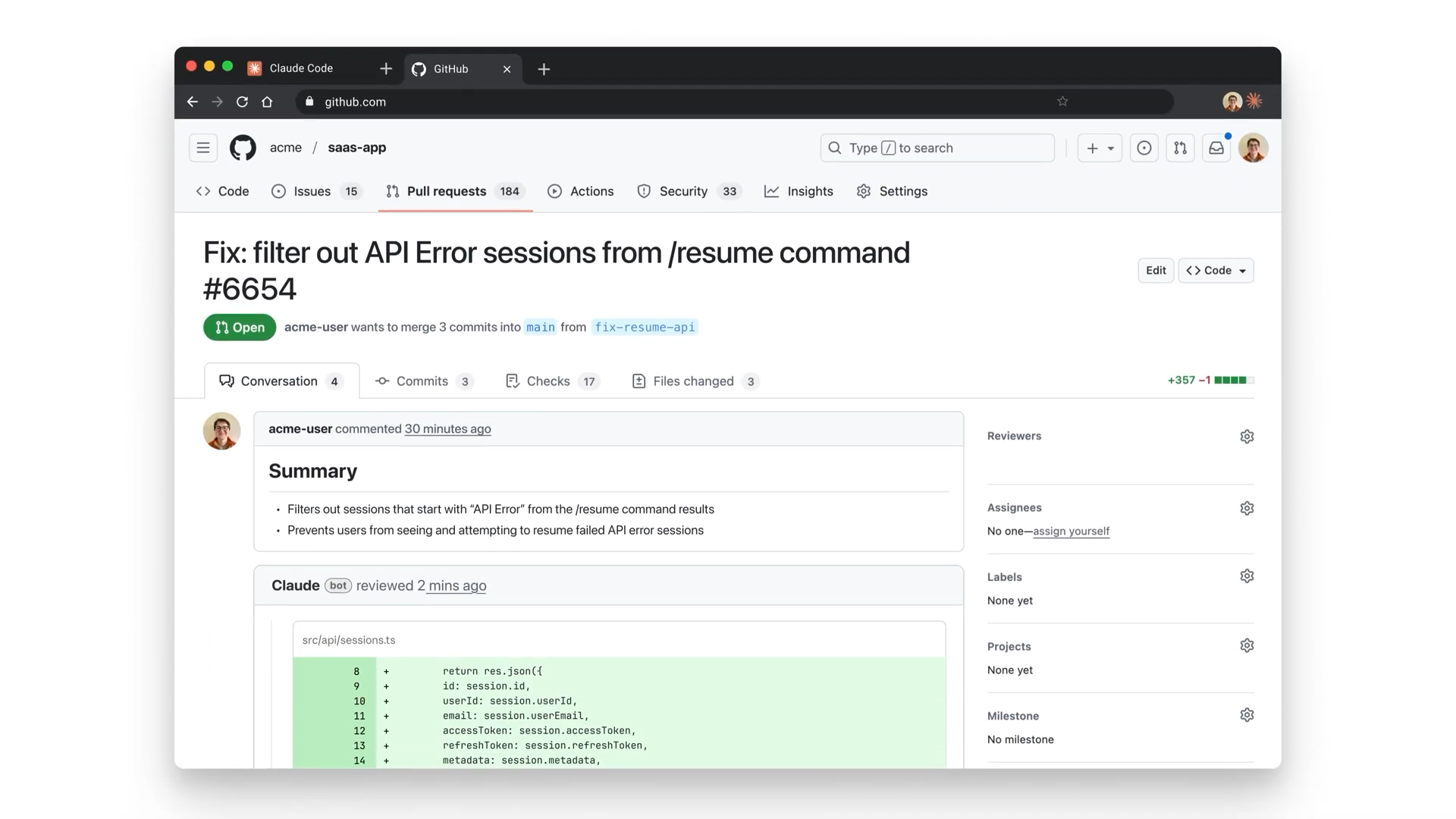
Then we created a pull request from the results:
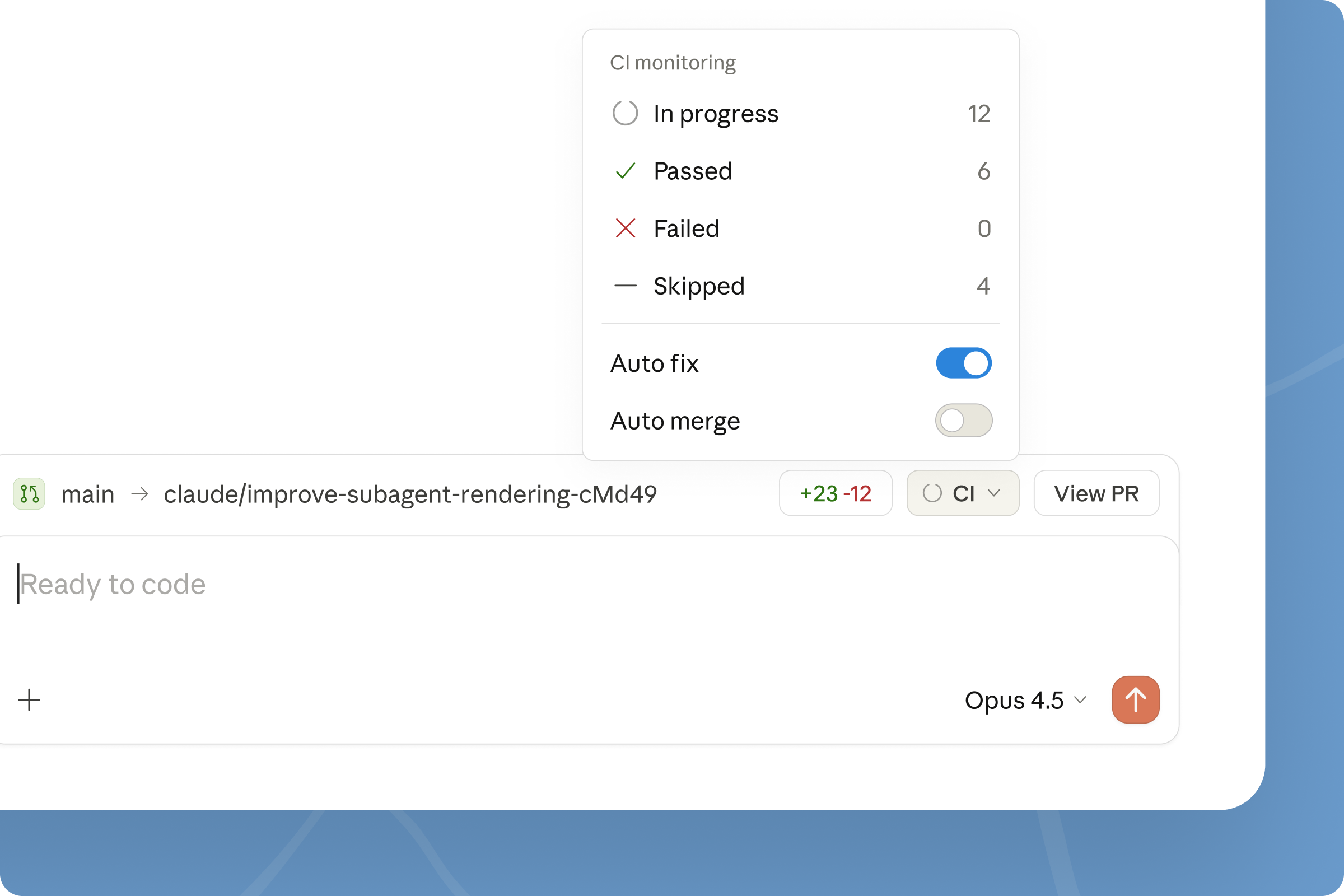
Immediately we create a pull request, Claude Code automatically started reviewing out changes:
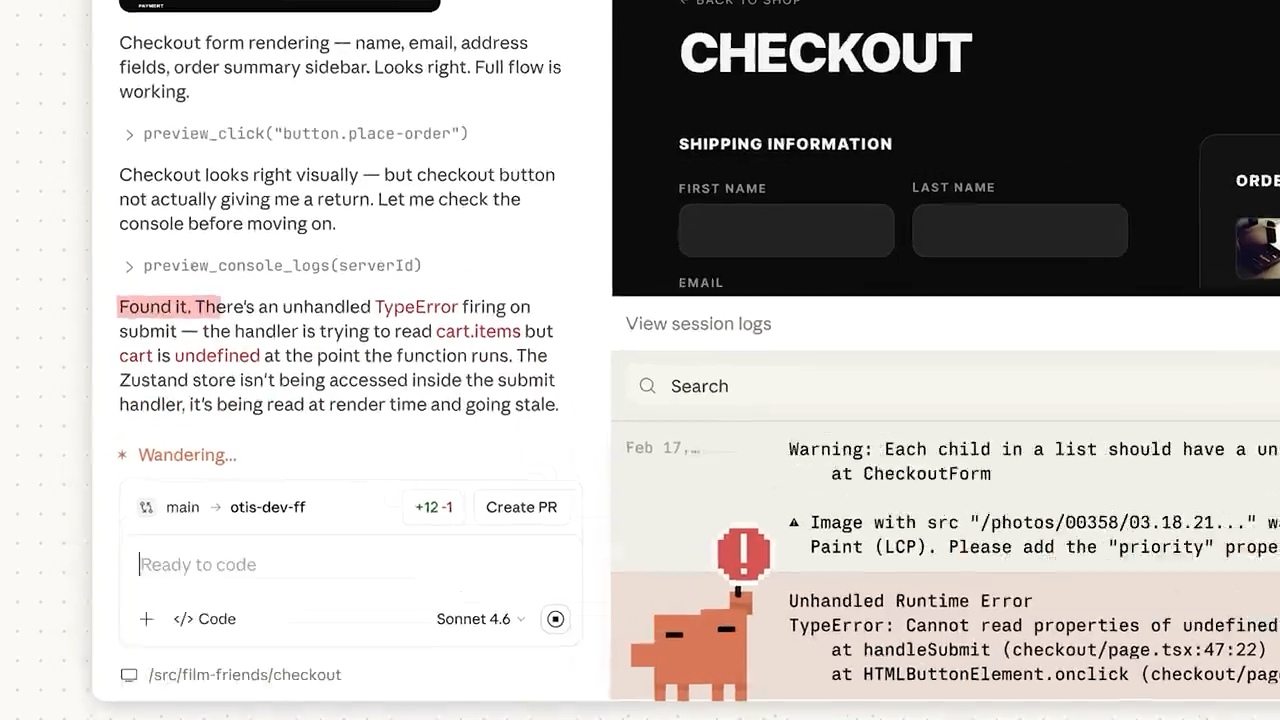
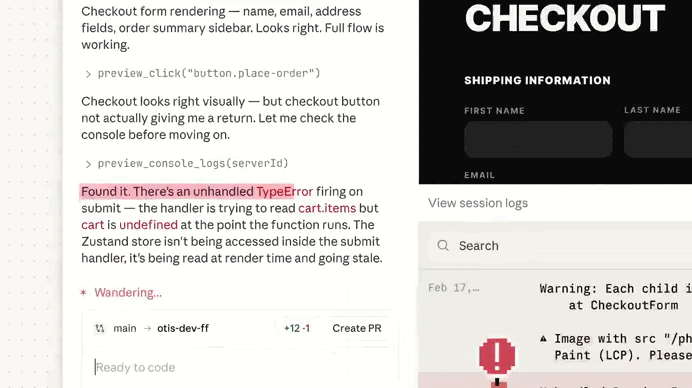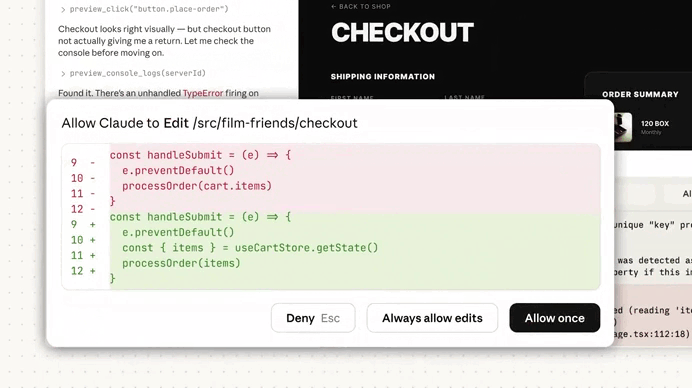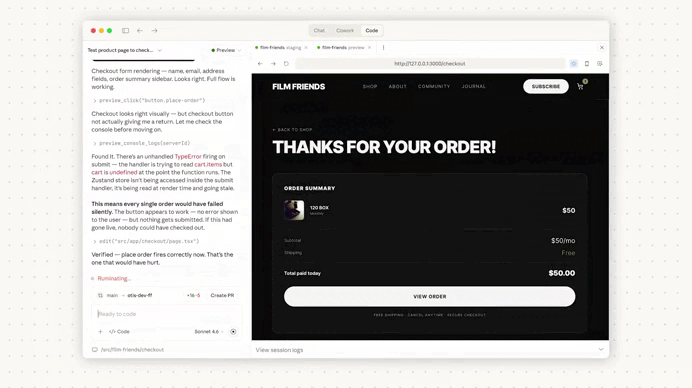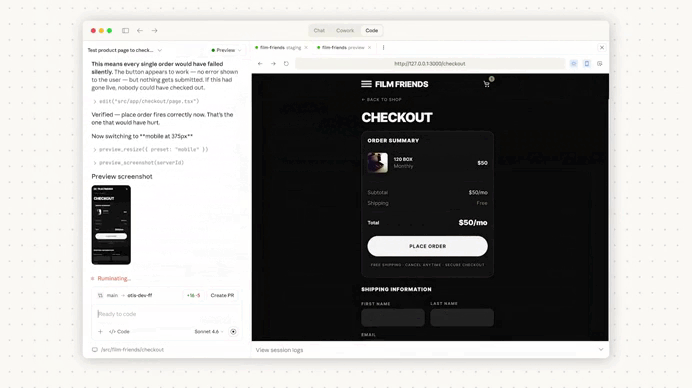
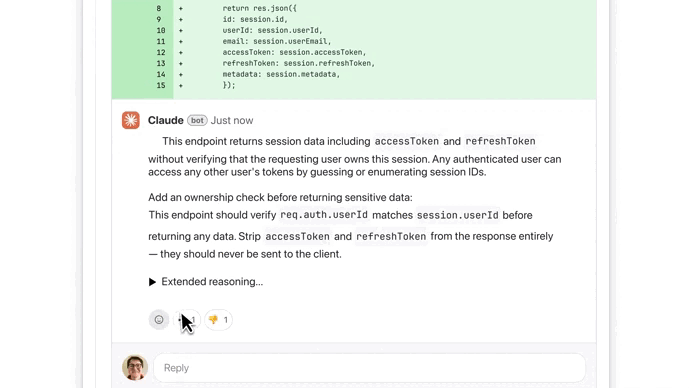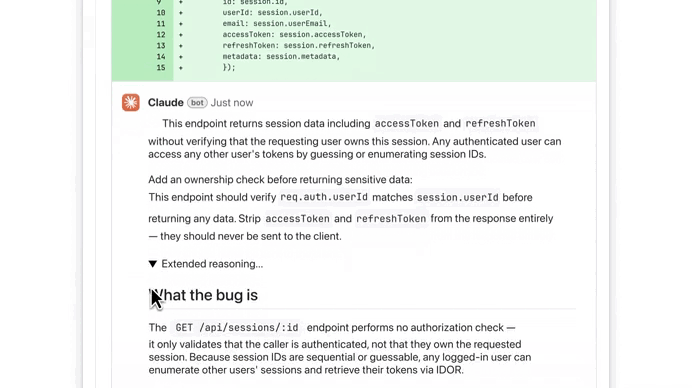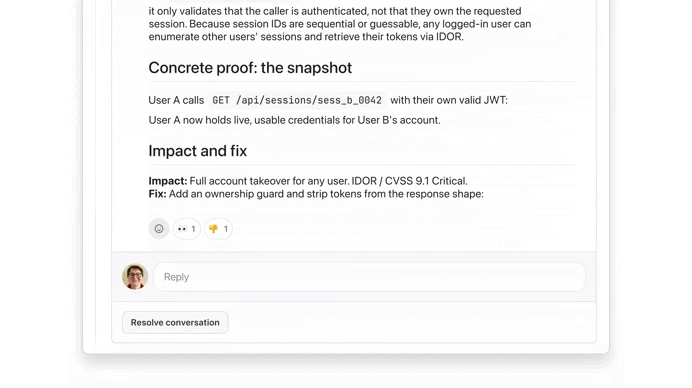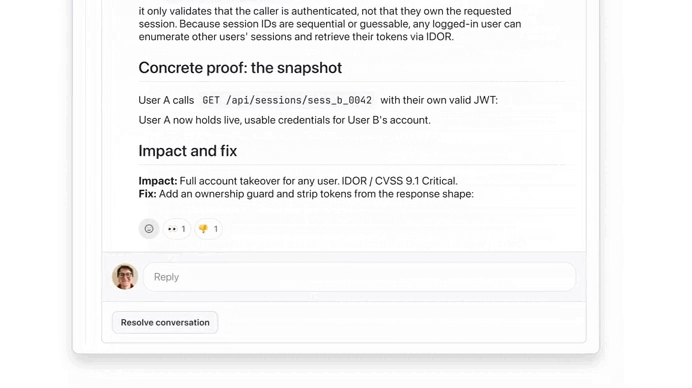
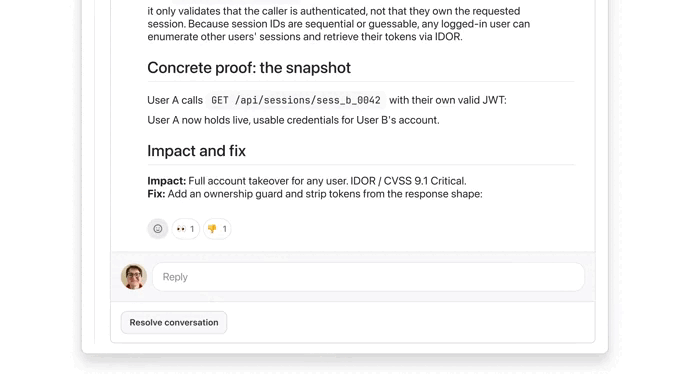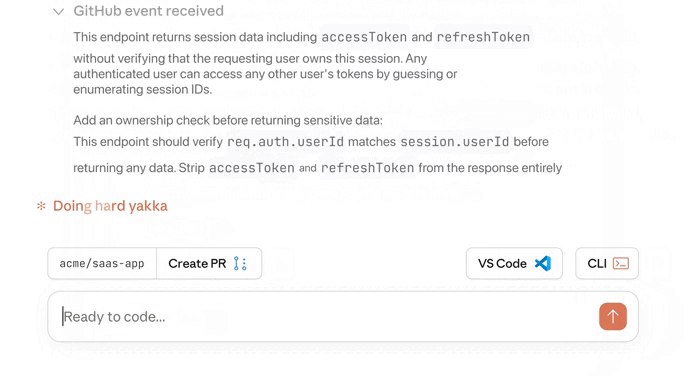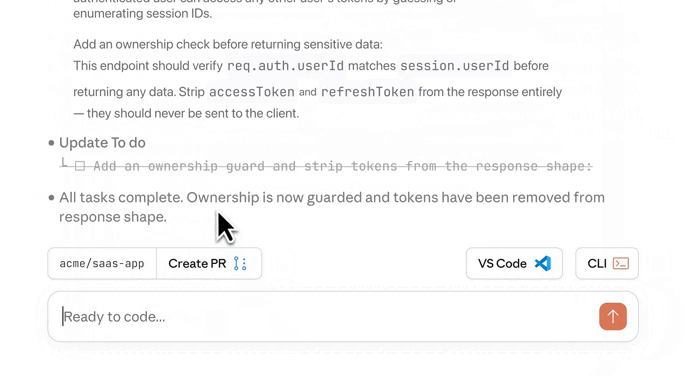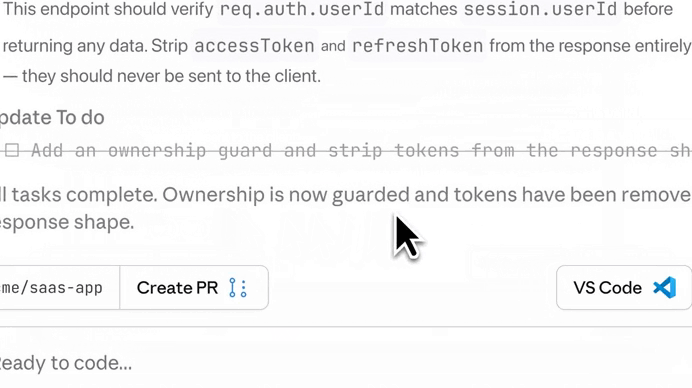
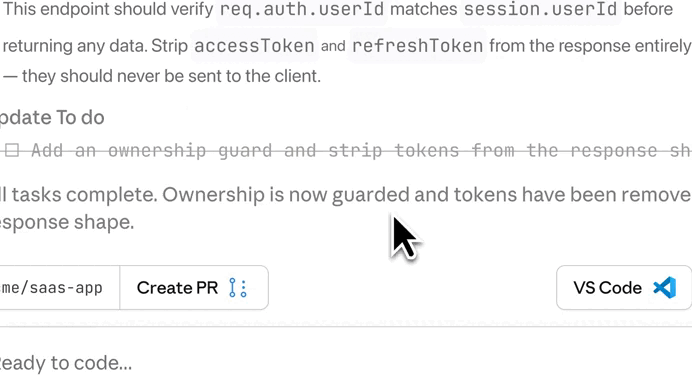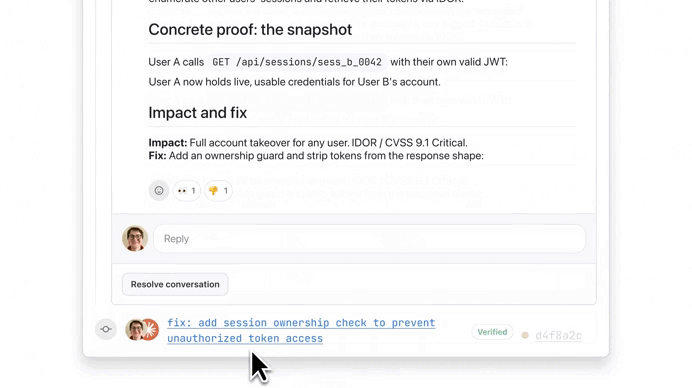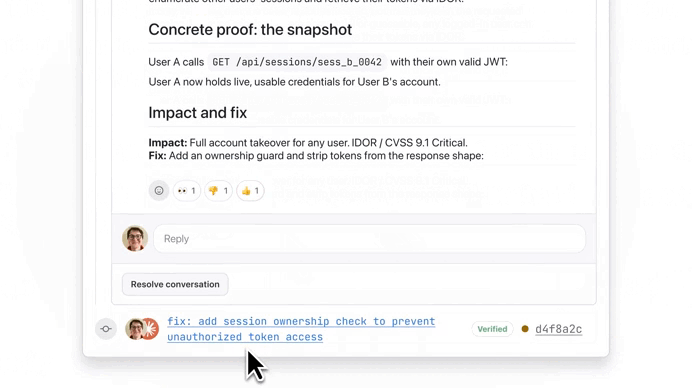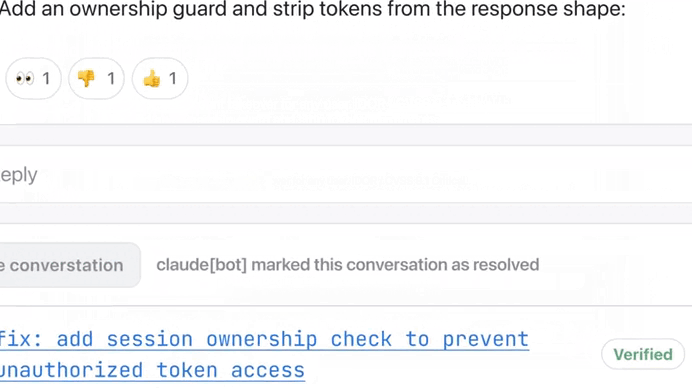
It found serious issue:
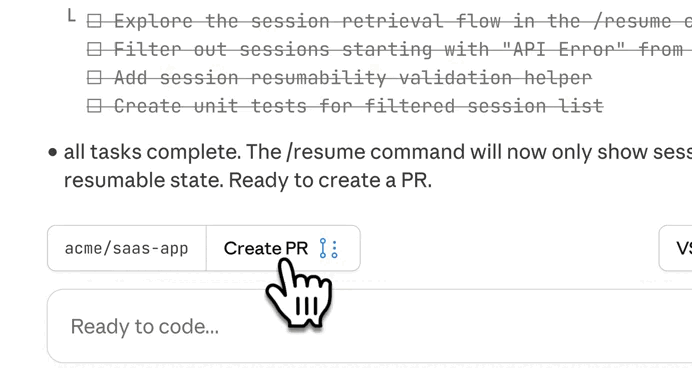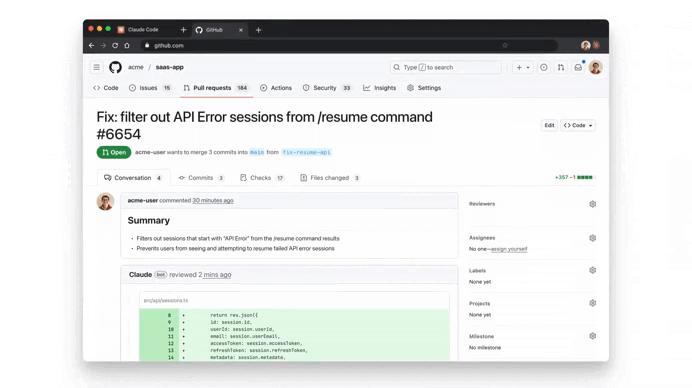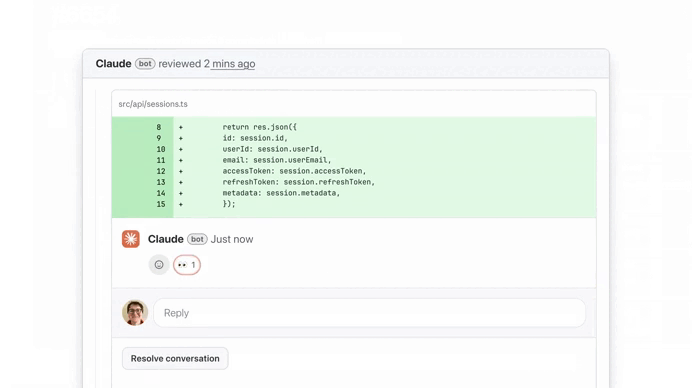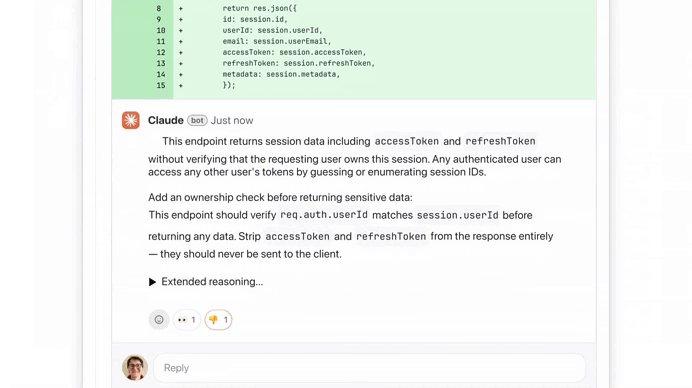
We used the button to see more details on this ownership check issue, thanks to Extended reasoning:
Claude started fixing the issue right away — it’s literally doing everything now — generate, test, review, fix… — while still giving you expert control to step in whenever you need to:
And just like that we fixed an issue that would have caused serious problems if it ever made its way to production:
AI coding tools dramatically increased how quickly developers produce code. But the problem now is reviewing it.
Anthropic’s new Code Review feature in Claude Code is here to help teams keep up with this massive surge in pull requests.
Instead of simply summarizing diffs, it analyzes PRs using multiple agents, verifies findings before posting comments, and prioritizes issues so developers can focus on what matters first.
Let’s check out all the key features of Claude Code Review and all the ways it benefits you as a developer.
1. Multi-agent architecture
One of the most interesting parts of Claude Code Review is how it analyzes pull requests.
When a PR opens, Claude dispatches a team of agents to examine the code simultaneously.
Each agent analyzes the change from a different angle, such as logic correctness, potential regressions, or security implications.
Rather than relying on a single pass through the diff, the system runs multiple analyses in parallel. This mirrors how human reviews often work: different reviewers tend to notice different classes of issues.
By distributing the work across specialized agents, Claude can explore several reasoning paths at once and surface findings that might otherwise be missed.
2. Verification loop
Finding potential bugs is only the first step. The system also tries to ensure those findings are reliable.
After agents identify issues, the results pass through a verification step.
Findings are cross-checked, duplicates are removed, and weaker or uncertain claims are filtered out before comments appear in the pull request.
This verification loop is important because AI tooling is only useful if developers trust the feedback. Without it, teams can end up spending more time validating AI comments than fixing real issues.
By verifying findings internally first, the system aims to reduce false positives and increase confidence in the comments that do appear.
3. Severity ranking
Not every issue uncovered during a review deserves the same level of attention.
Claude Code Review prioritizes findings using a severity ranking system
Higher-impact issues are surfaced first, while lower-priority suggestions are categorized separately.
This allows developers to quickly identify which problems are most important to address before merging.
Instead of scanning a long list of comments, engineers can immediately focus on issues that could affect correctness, reliability, or security.
4. Scales based on PR size
Claude’s review process also adapts based on the size and complexity of the pull request.
Small changes receive a relatively quick analysis, while large changes trigger deeper inspection.
A minor change of a few lines might get a fast scan, while a large refactor can trigger a much more thorough review involving multiple agents and a longer analysis window.
This dynamic approach ensures that larger, higher-risk changes receive proportionally more scrutiny.
Why this matters
1. Solving the AI review bottleneck
AI coding tools like Claude Code and Cursor have made it possible for developers to generate code far faster than before.
But human review capacity hasn’t scaled at the same rate.
The result is a new bottleneck: pull requests accumulate, reviewers skim rather than deeply analyze changes, and subtle issues slip through. AI-powered review helps address this by scaling analysis alongside code generation.
2. Catching vibe coding logic errors
AI-assisted development often introduces subtle logic bugs that look perfectly reasonable at first glance.
In internal testing, Anthropic reported that Claude caught a one-line authentication bug that appeared routine to human reviewers but would have broken production security.
These types of issues — small mistakes hidden inside otherwise plausible code — are exactly where deeper automated review can add value.
3. Higher signal, lower noise
Most CI pipelines already produce large amounts of automated feedback: lint warnings, formatting issues, dependency alerts, and more.
Claude Code Review focuses primarily on logic errors and security risks, rather than stylistic issues already handled by other tools. The goal is fewer comments, but more meaningful ones.
4. Context-aware security
Because the system analyzes code within the broader repository context, it can also detect latent bugs — issues that already exist but are exposed by a new change.
This kind of context-aware analysis allows the system to identify problems that wouldn’t appear in simple diff-based review.
Ways developers can use it
Claude Code Review fits best as an additional layer in the development workflow rather than a replacement for human reviewers. Some practical ways teams can use it include:
1. Pre-review screening
Run Claude on a PR before assigning human reviewers. It can catch obvious logic or security issues early, allowing engineers to fix them before the PR reaches teammates.
2. Reviewing large refactors
Massive refactors and generated changes are difficult for humans to review thoroughly. Claude’s multi-agent analysis can help identify regressions or subtle breakages hidden in large diffs.
3. Reviewing AI-generated code
When large chunks of code are generated by tools like Claude Code or Cursor, teams can use automated review to sanity-check the logic before merging.
4. Security-focused reviews
Because the system analyzes repository context, it can help surface potential authentication, permission, or data handling issues that might not be obvious in a quick diff review.
5. Catching latent bugs
Sometimes a change exposes problems that already existed elsewhere in the codebase. Claude can flag these “pre-existing” issues so teams can decide whether to fix them during the current PR.
Claude Code’s new Code Review feature reflects a broader shift in software development.
As AI accelerates code generation, review systems also need to evolve. Multi-agent analysis, verification loops, and context-aware review are attempts to scale code scrutiny without scaling review workload.
If tools like this prove reliable in real-world teams, they could become an important part of the modern code review stack.