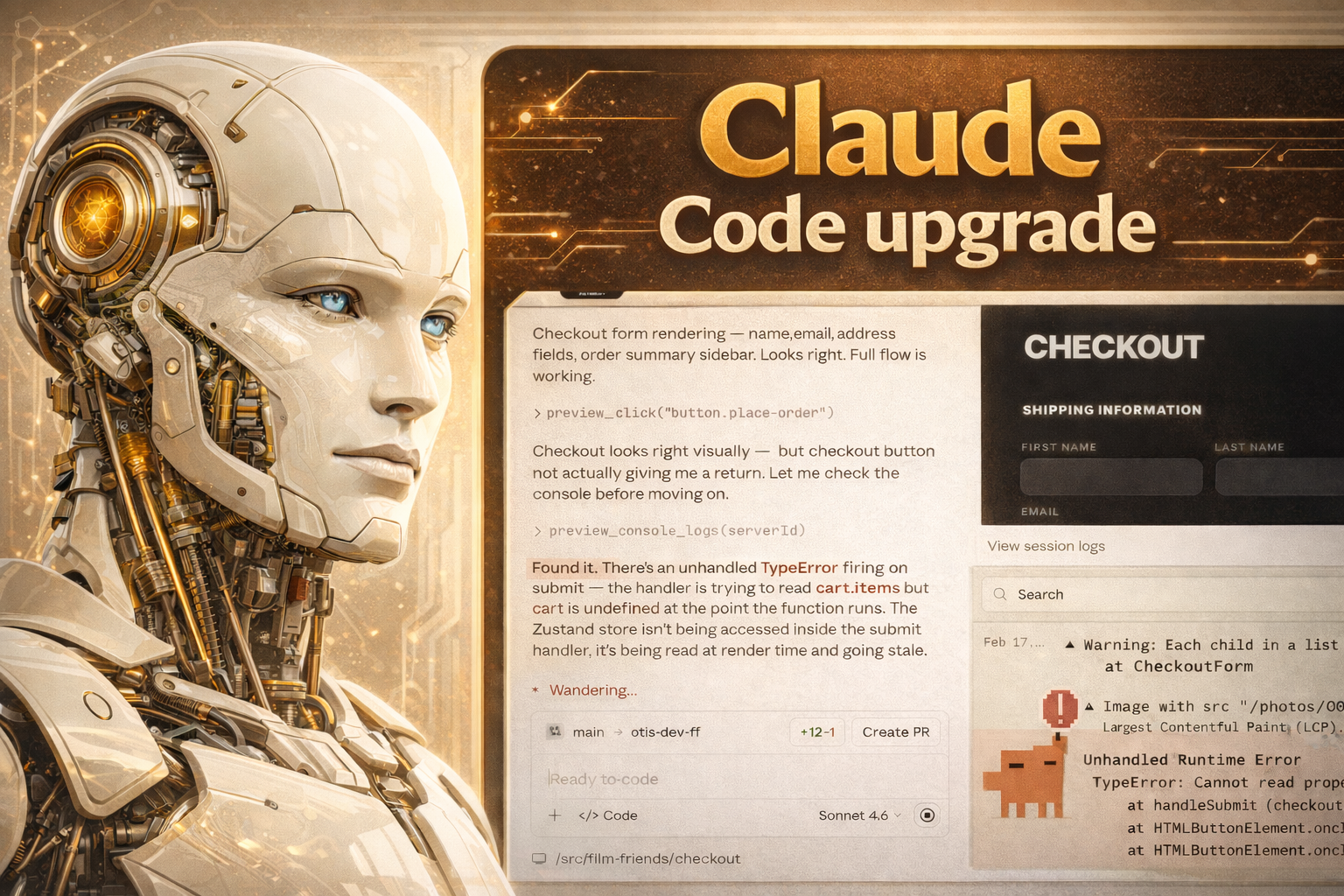
How Claude Code’s new auto-memory feature solves a major problem with AI coding agents
Many AI coding tools have always had one frustrating flaw: they forget everything the moment a session ends.
Claude Code’s new auto-memory feature changes that by letting the assistant retain useful project knowledge between sessions, turning it from a stateless helper into something closer to a long-term collaborator.
Instead of constantly re-explaining your setup, conventions, and debugging lessons, Claude can now carry that context forward automatically.
The result is a workflow that feels less like starting over every time—and more like picking up exactly where you left off.
How it works
Passive capture
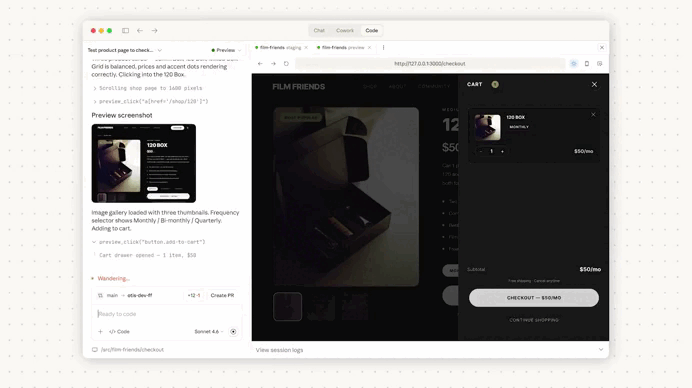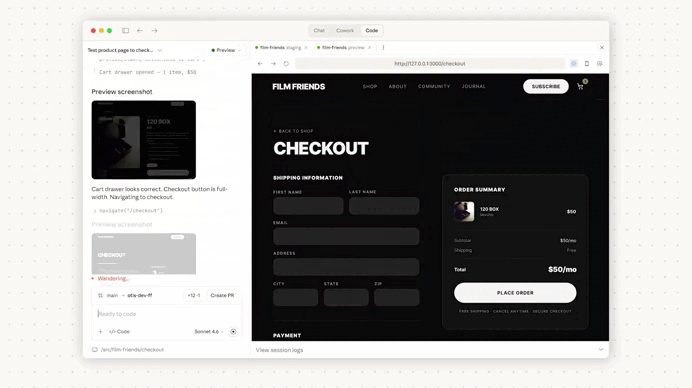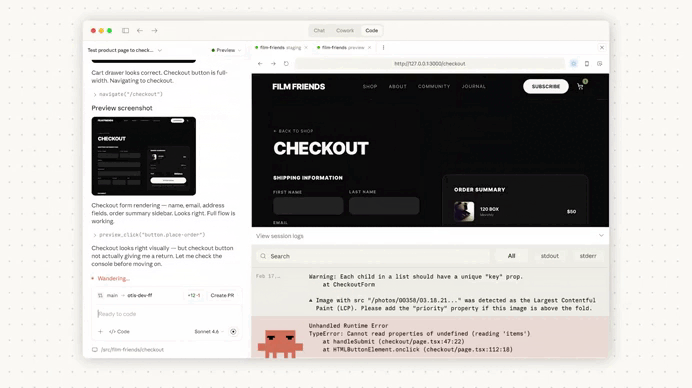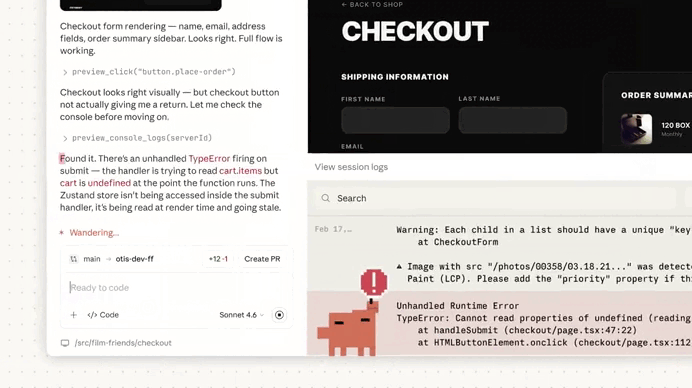
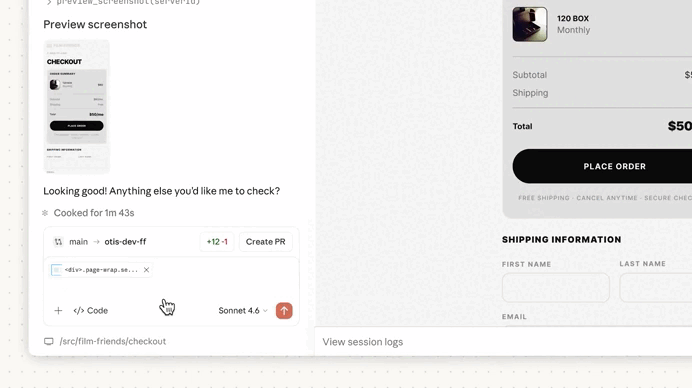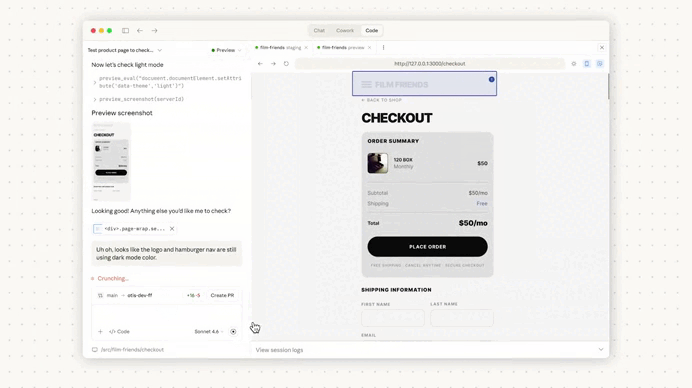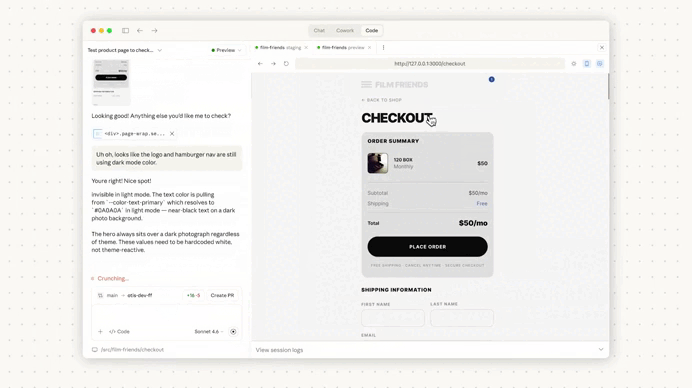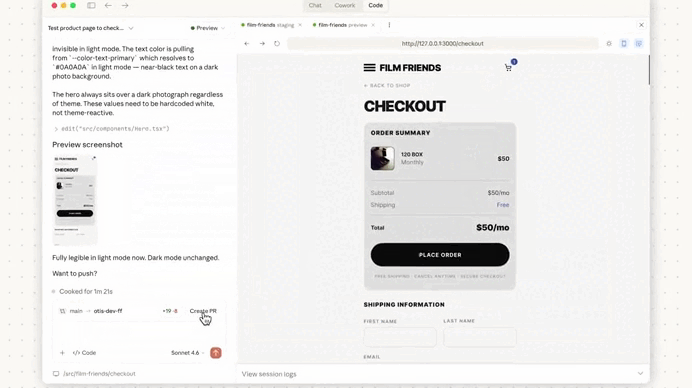
Auto-memory runs quietly in the background.
As you work, Claude identifies recurring patterns, debugging insights, and workflow preferences, then stores them in a local markdown memory file.
Over time it begins capturing things like:
- how your team runs tests
- which package manager the repo uses
- conventions for naming services or components
- recurring debugging lessons
- local environment quirks
Instead of manually documenting every small lesson, Claude gradually builds a lightweight project memory as you work.
This is important because most of these details are never formally documented—they’re just things developers repeat in every AI session.
Automatic injection
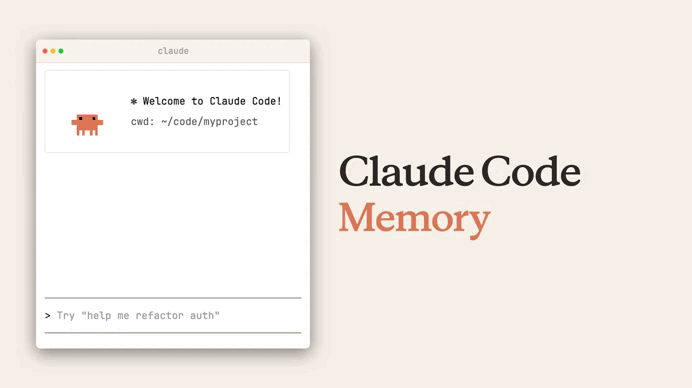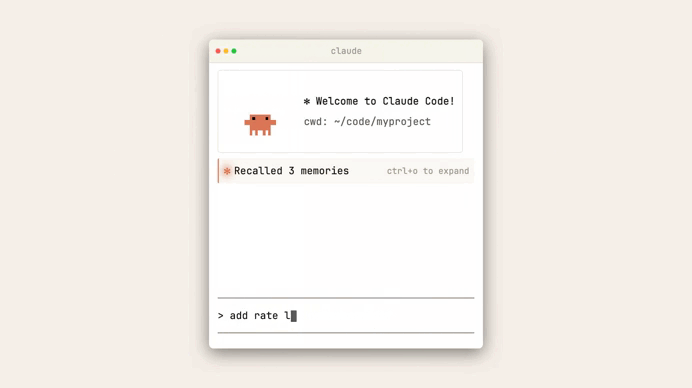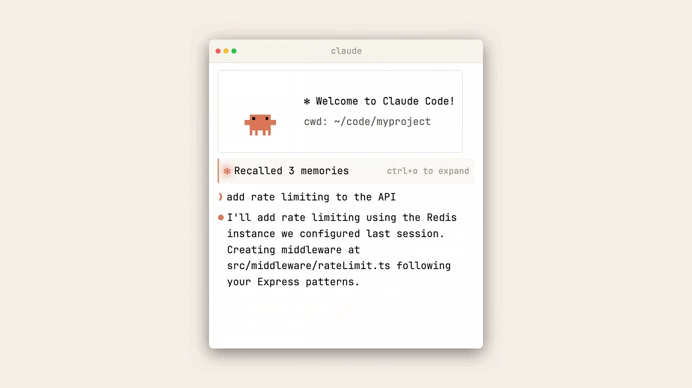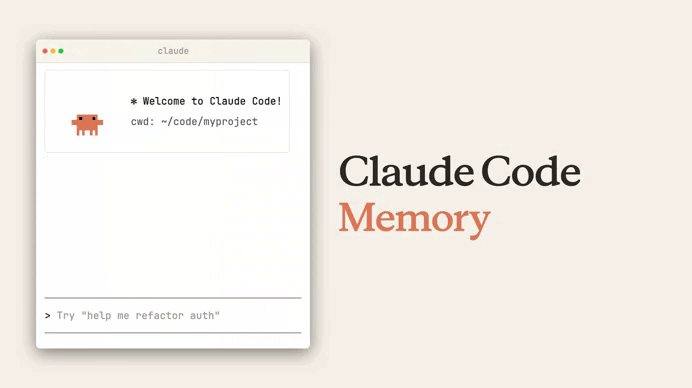
The real value appears when you start a new session.
Claude immediately reads the project memory file, which effectively warms up its context before any interaction begins.
This means Claude can start with awareness of things like:
- your preferred test command
- project tooling choices
- known debugging pitfalls
- team conventions
Instead of:
- rescanning large files to rediscover patterns
- asking you the same setup questions
- requiring repeated explanations
The memory acts like a compact summary of the project’s operational knowledge.
User control
Persistent memory only works if developers can control it.
Claude provides a /memory command that lets you:
- review saved memory
- edit stored information
- delete outdated entries
- disable auto-memory if needed
This matters because project reality changes. For example:
- a workaround might become obsolete after a refactor
- a naming convention may evolve
- debugging notes may no longer apply
With direct access to the stored markdown, you can prune outdated knowledge and keep the memory accurate.
Why it matters
Zero-day productivity
The biggest improvement is eliminating session amnesia.
Without persistent memory, every new session often starts with explanations like:
- how to run the test suite
- how the repo is structured
- which framework conventions your team follows
Auto-memory removes most of that overhead.
Each new session begins closer to a continuation than a restart, which means less setup and faster time to useful work.
Contextual accuracy
A lot of critical engineering knowledge never appears in documentation.
It lives in tribal knowledge, like:
- the one bug that only happens locally
- the dependency a test suite silently requires
- a naming pattern everyone follows informally
- a specific workaround discovered during debugging
Auto-memory helps preserve these small but important details so Claude operates with real project context, not just what’s written in a README.
Token efficiency
There’s also a practical benefit related to context usage.
Instead of repeatedly:
- scanning large files
- reconstructing patterns from scratch
- consuming prompt space on setup explanations
Claude can rely on a compact memory summary.
That helps:
- conserve context window space
- reduce redundant prompts
- make longer development sessions more efficient
Agentic continuity
This becomes even more useful in multi-agent workflows.
If you use subagents for delegated tasks, shared project memory helps ensure:
- the main agent and subagents follow the same conventions
- debugging discoveries persist across tasks
- agents operate with consistent assumptions about the project
In larger codebases, that consistency can prevent subtle errors and reduce friction between automated tasks.
Final thoughts
Auto-memory isn’t a flashy feature—but it solves a real problem in AI coding workflows.
By combining:
- passive knowledge capture
- automatic context injection
- direct user control
Claude Code becomes less forgetful and more useful over time.
For developers, the result is simple:
- less repetition
- better recall of project details
- a coding assistant that actually remembers how your project works.