Software development is changing fast and AI is at the center of it.
Today’s best developers aren’t just writing code — they’re collaborating with intelligent agents to think, plan, and build differently.
There’s a shift happening in how apps are imagined, designed, and brought to life.
Developers who know how to work with AI can move faster, think bigger, and build smarter — from the very first spark of an idea all the way to a finished product.
Generate requirements
AI helps you systematically break down a high-level idea into concrete, manageable requirements.
Instead of getting stuck in a brainstorming loop, you can use an AI agent to act as a consultant, asking clarifying questions and suggesting a comprehensive list of features.
With this you identify potential edge cases and missing components early in the process.
What the AI can do
- Generate a list of functional and non-functional requirements.
- Ask clarifying questions to refine your initial idea.
- Analyze your requirements for potential contradictions or missing details.
- Suggest features based on industry standards and best practices.
Example prompt
- “I want to build a social media app for fitness enthusiasts. What are the core features I’ll need for this app? Categorize them by user roles (e.g., individual user, admin).”
- “Given the requirements for a real-time chat feature, what are the potential technical challenges and non-functional requirements I should consider, such as scalability and security?”
- “Act as a product manager. I’ve defined the following features for my to-do list app: user authentication, task creation, task deletion, and task editing. What is missing? What other features would make this a more complete product?”
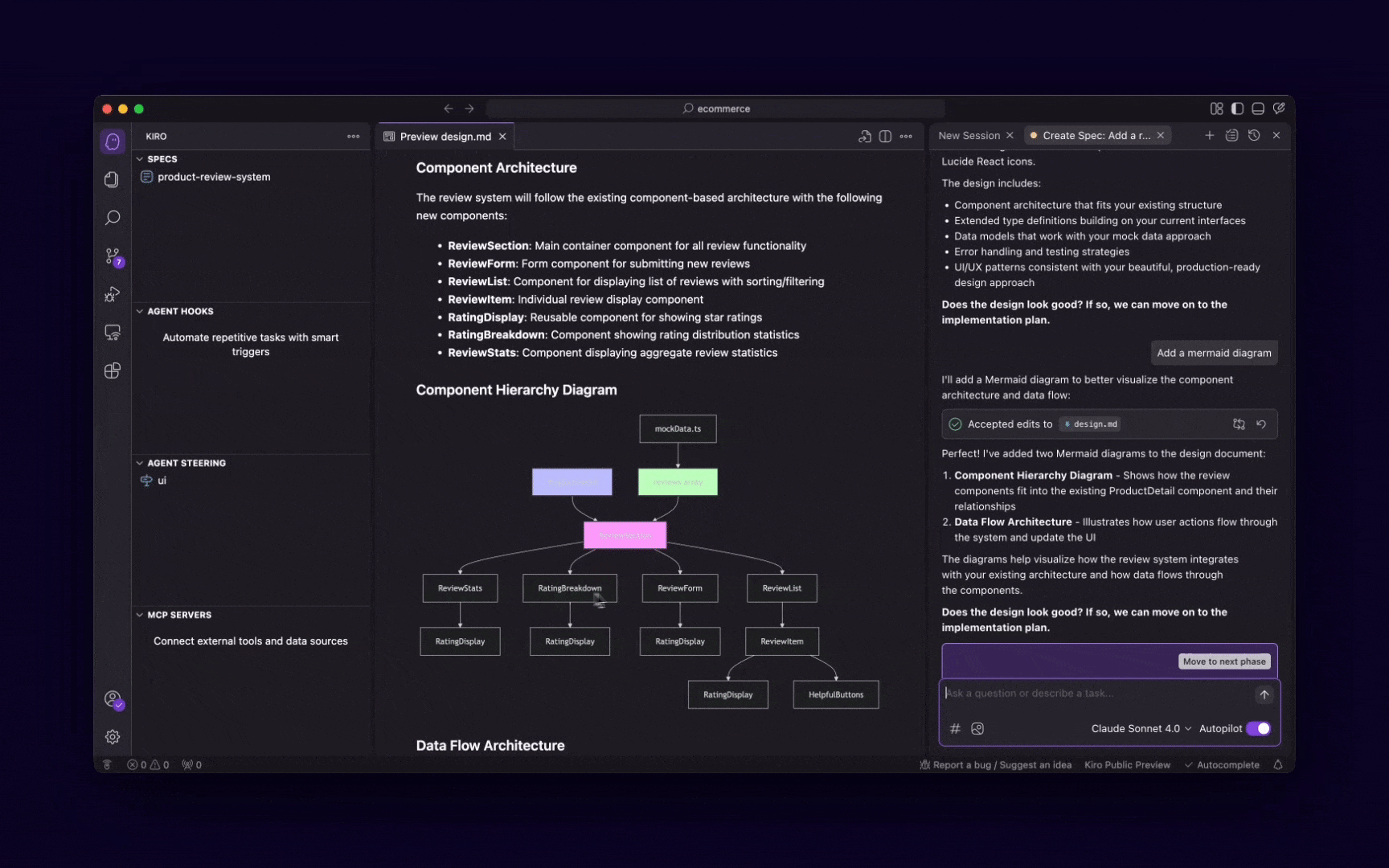
Design and plan
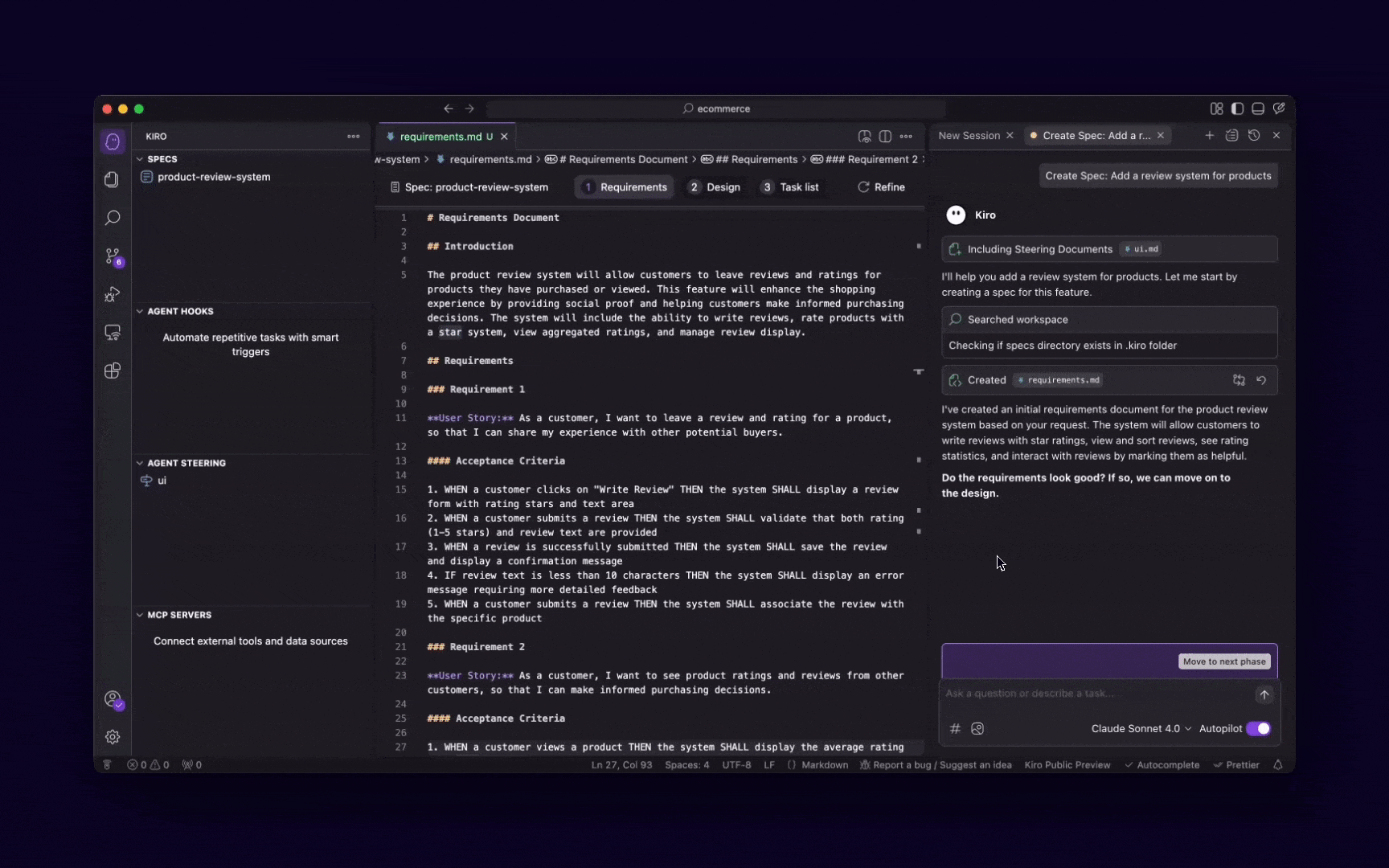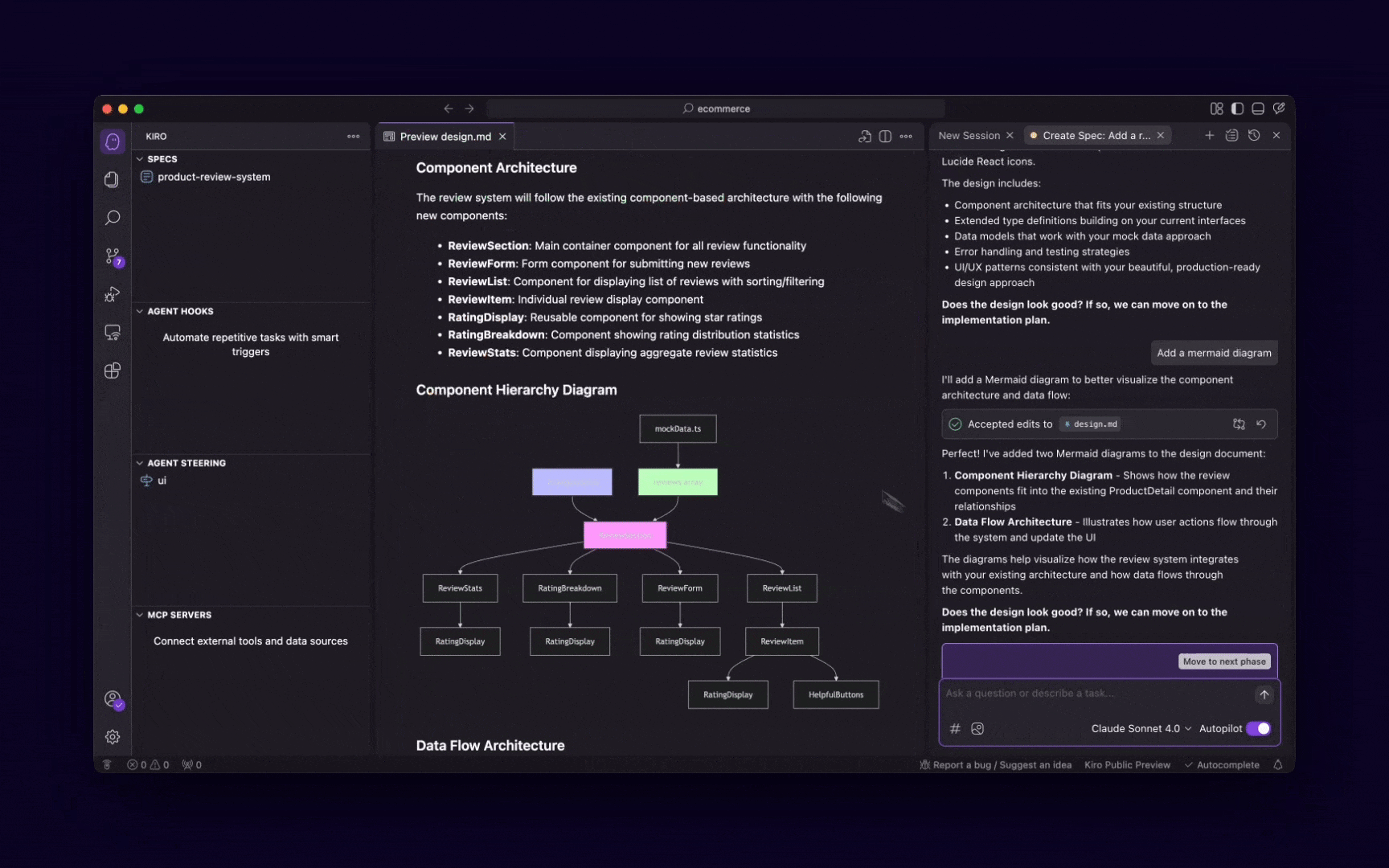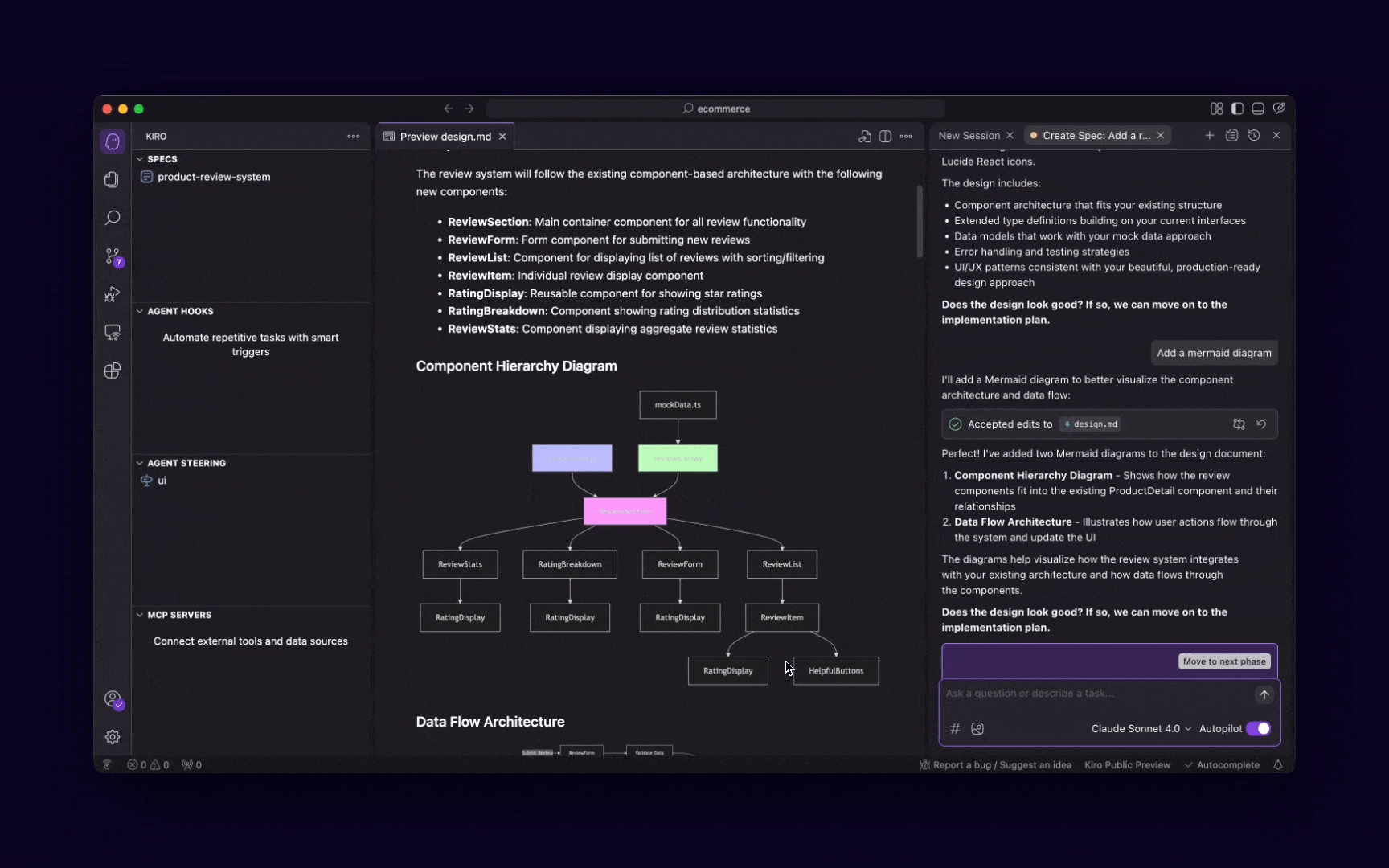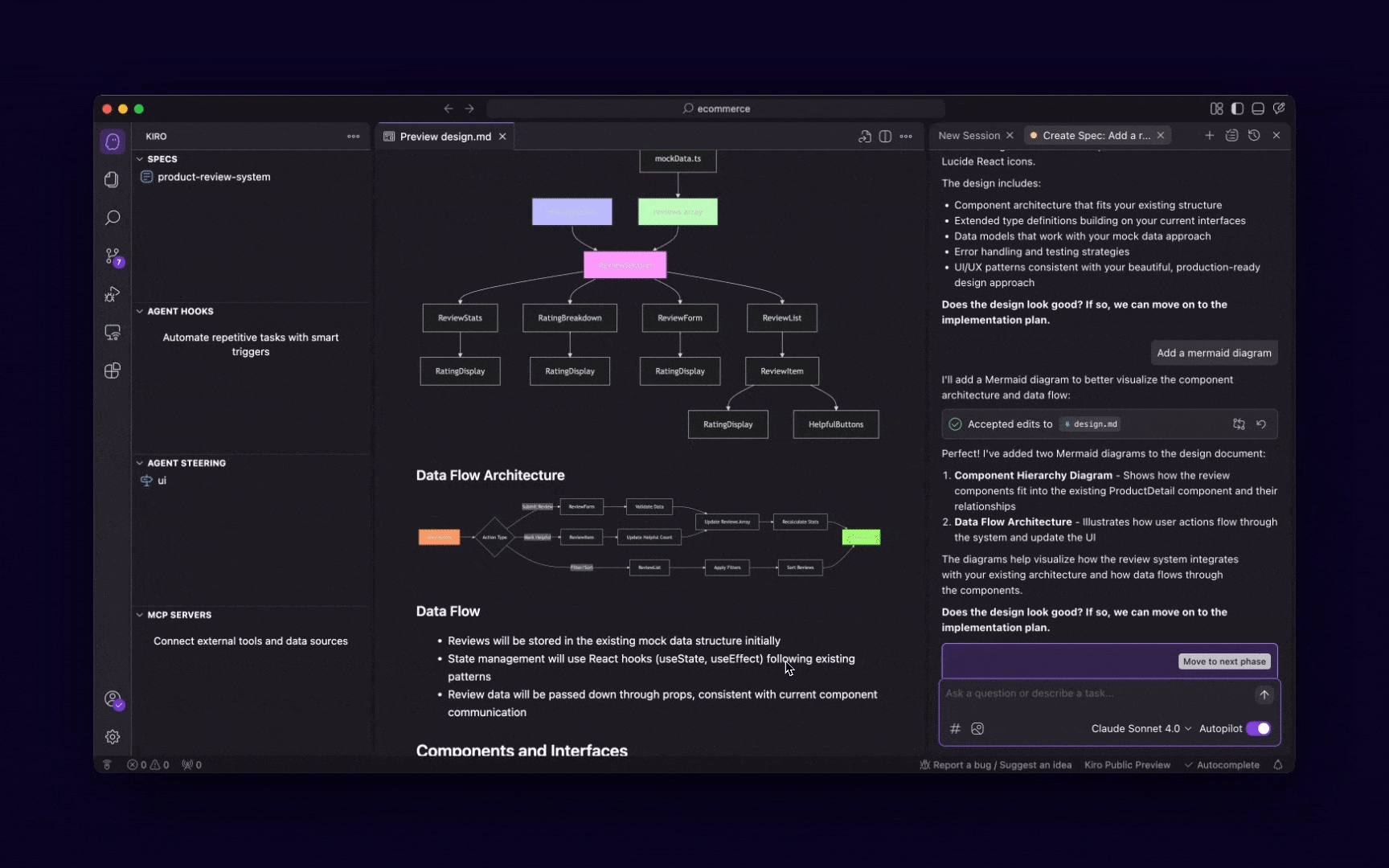
Once you have your requirements, an AI agent can help you with the architectural design, data modeling, and even UI/UX wireframing. It can suggest design patterns, database schemas, and user flows, acting as a virtual architect or designer.
What the AI can do
- Propose an application architecture (e.g., monolithic, microservices).
- Design a database schema based on your app’s features.
- Generate user flow
- Suggest UI components and design patterns for specific screens.
Example prompts
- “Design a scalable and secure backend architecture for a real-time messaging app. It should support millions of concurrent users and handle high-volume data traffic.”
- “Based on the following features for a food delivery app: user profiles, restaurant listings, order tracking, and payment processing, generate a detailed database schema using PostgreSQL.”
- “Give me an UI flow for the user registration and login process of a mobile app. The flow should include screens for sign-up, email verification, password reset, and a successful login state.”
- “Generate an example of a component for a social feed that uses the React framework. The component should display posts with images, likes, and comments.”
Prototype rapidly
When it’s time to build AI can rapidly create the foundational structure or “scaffolding” of your app.
This includes generating project directories, configuration files, and basic API endpoints, allowing you to start building on a solid foundation without the manual setup overhead.
What the AI can do
- Generate a project structure for a specific framework (e.g., a Next.js app with a Tailwind CSS setup).
- Create a basic API with CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) endpoints.
- Write configuration files for linters, formatters, and build tools.
Example prompts
- “Create the file and folder structure for a full-stack e-commerce application using Next.js, Express.js, and MongoDB.”
- “Generate a basic REST API in Python using Flask. The API should have endpoints for a ‘products’ resource, including /products (GET), /products/:id (GET), and /products (POST).”
- “Set up a new React project in the current directory. Include the necessary dependencies for state management with Zustand and routing with React Router.”
Create and build
This is where AI shines as a pair programmer.
Go beyond simple functions and files — ask the AI to implement entire features at a high level and stay focused on the bigger picture.
What the AI can do
- Write feature-complete code blocks based on a description.
- Integrate different services or APIs.
- Refactor existing code to improve performance or readability.
- Generate test data for specific functions or features.
Example prompts
- “Implement the ‘user registration’ feature. It should take a username and password, validate them, hash the password, and store the new user in the database. Use Express.js and Mongoose.”
- “Create a ‘search functionality’ for a list of blog posts. The search should be case-insensitive and match against the post’s title and content. Write this using React with hooks.”
- “Using the
requestslibrary in Python, write a function to fetch weather data from the OpenWeatherMap API for a given city and parse the JSON response.”
Testing
AI can automate and enhance your testing process by generating test cases, identifying potential bugs, and even creating entire test suites. This helps you catch errors early and ensures your code is robust.
What the AI can do
- Generate unit tests for functions or components.
- Create integration tests to verify interactions between different parts of your application.
- Find edge cases and potential failure scenarios for your code.
- Write end-to-end tests for critical user flows.
Example prompts
- “Write Jest unit tests for the following
calculateTaxfunction. Include tests for positive cases, zero values, and invalid inputs like negative numbers or strings.” - “Generate integration tests for the user authentication flow to ensure that a new user can successfully register and log in.”
- “Analyze the
updateShoppingCartfunction for potential bugs or race conditions, and suggest test cases to expose them.” - “Write a Playwright test script to simulate a user adding an item to a cart and completing the checkout process on an e-commerce website.”
Code review
Even for flawless code, an AI can provide an objective second opinion. It can check for style consistency, potential security vulnerabilities, and opportunities for optimization that you might have missed.
What the AI can do
- Check for adherence to specific style guides (e.g., Airbnb JavaScript Style Guide).
- Identify code smells, anti-patterns, and potential performance bottlenecks.
- Suggest refactoring to make the code cleaner and more efficient.
- Detect common security vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS).
Example prompts
- “Review the following code for any security vulnerabilities, especially in handling user input.”
- “Analyze this file and suggest ways to simplify the logic and improve its readability. Use clear, concise language in your suggestions.”
- “Perform a code review of this pull request. Check for adherence to SOLID principles and clean code practices. Also, provide a brief summary of the changes and your overall assessment.”
- “Suggest a better name for the
processDatafunction and provide an explanation for why the new name is more appropriate.”
Documentation
One of the most tedious parts of coding, documentation, can be almost fully automated with AI. A well-prompted AI can generate a wide range of documentation, from in-line code comments to comprehensive API guides.
What the AI can do
- Write clear and concise JSDoc comments for functions and classes.
- Generate a README.md file for a project, including setup instructions and usage examples.
- Create API documentation based on your codebase.
- Summarize a complex code block or a project’s purpose in a non-technical way.
Example prompts
- “Write JSDoc comments for the
fetchUserDatafunction, including a description of its purpose, parameters, and what it returns.” - “Generate a README.md file for a Python project that uses Flask and SQLAlchemy. The README should include an overview, installation instructions, how to run the app locally, and a basic API endpoint reference.”
- “Act as a technical writer. Explain how the
PaymentServiceclass works in simple, clear terms for a new developer joining the team.” - “Generate a
CHANGELOG.mdfor this project based on the git commit history since the last release.”