To scroll to an element after render on React:
- Set a ref on the element.
- Create a
useEffecthook to run code just after the component mounts. - Call
scrollIntoView()on the ref object inuseEffect.
import { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
export default function App() {
const ref = useRef(null);
const scrollToElement = () => {
ref.current?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
};
useEffect(() => {
scrollToElement();
}, []);
return (
<div>
<div style={{ height: '150rem' }} />
<div ref={ref} style={{ backgroundColor: 'blue', color: 'white' }}>
Coding Beauty
</div>
<div style={{ height: '150rem' }} />
</div>
);
}
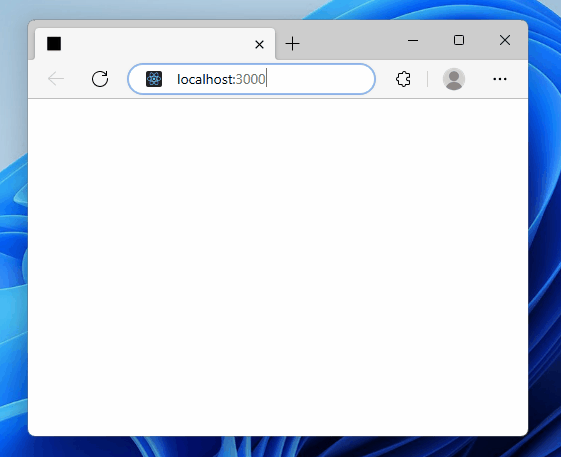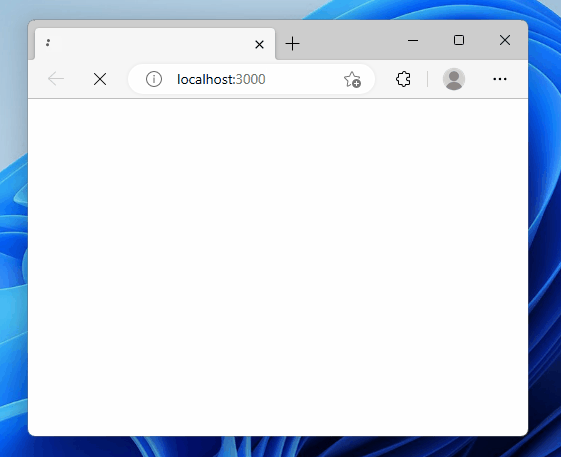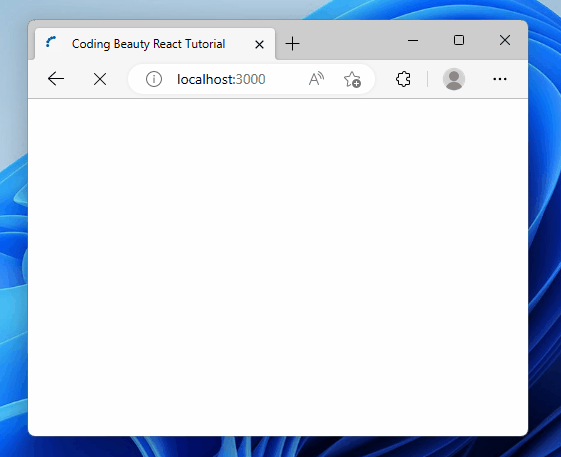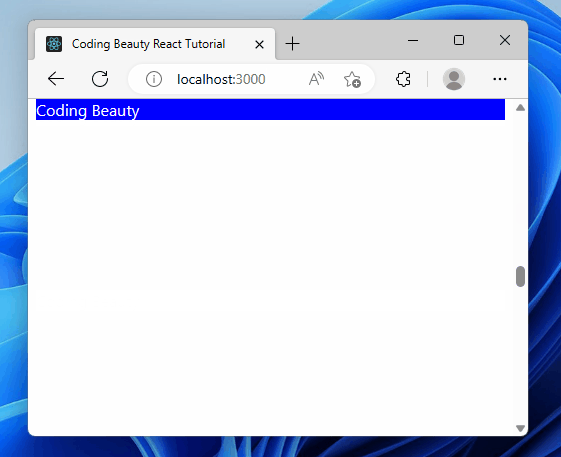
Scrolling to an element after the page loads in React helps users quickly find important information, fix errors, and is useful for those who use special software to navigate the web.
We create a ref object with the useRef hook and assign it to the ref prop of the target div element. Doing this sets the current property of the ref object to the DOM object that represents the element.
useRef returns a mutable object that maintains its value when a component updates. Also, modifying the value of this object’s current property doesn’t cause a re-render. This is unlike the setState update function return from the useState hooks.
The useEffect hook performs an action after the component renders, and when one or more of its dependencies change. We passed an empty dependencies array ([]) to make sure that action only runs when the component mounts.
In useEffect, we call the scrollIntoView() method on the ref of the target div element to scroll down to it and display it to the user.
We set the behaviour option to smooth to make the element scroll into view in an animated way, instead of jumping straight to the element in the next frame (auto). auto is the default.
Scroll to element on click in React
Learn more: How to Scroll to an Element on Click in React
We can do something similar to scroll to an element on click in React:
- Set a ref on the target element.
- Set a click listener on the element meant to cause the scroll.
- In the click event listener, call the
scrollIntoView()method on therefobject.
import { useRef } from 'react';
export default function App() {
const ref = useRef(null);
const handleClick = () => {
ref.current?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={handleClick}>Scroll to element</button>
<div style={{ height: '150rem' }} />
<div ref={ref} style={{ backgroundColor: 'lightblue' }}>
Coding Beauty
</div>
<div style={{ height: '150rem' }} />
</div>
);
}
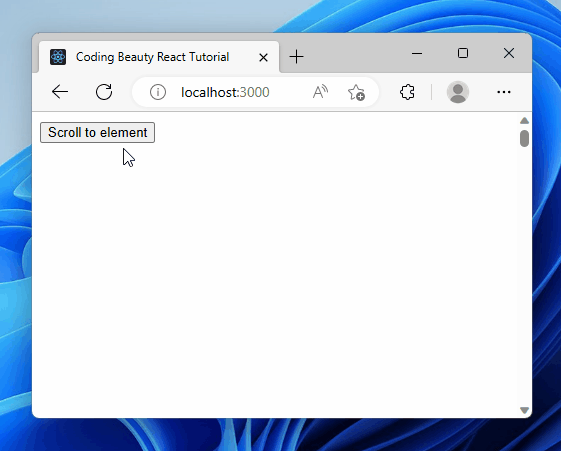
Scrolling to an element on click improves user experience by allowing for quick navigation, especially for long lists or pages with multiple sections. It can also add a touch of interactivity through smooth-scrolling animations.
We create a ref object with the useRef hook and assign it to the ref prop of the checkbox input. Doing this sets the current property of the ref object to the DOM object that represents the target element.
useRef returns a mutable object that retains its value when a component updates. Changing the value of this object’s current property doesn’t cause a re-render. This is different from the setState update function that useState returns.
We use the onClick on the button to a click listener to it. So, this listener will be called when the user clicks the button.
const handleClick = () => {
ref.current?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
};In the handleClick listener, we call the scrollIntoView() method on the ref of the target div element to scroll down to it and display it to the user.
As before, we set the behaviour option to smooth to make the element scroll into view in an animated way, instead of jumping straight to the element in the next frame – auto. auto is the default.
Scroll to dynamic element on click in React
We can also scroll to a dynamically created element in React.
import { useRef, useState } from 'react';
const allFruits = [
'Apples',
'Bananas',
'Oranges',
'Grapes',
'Strawberries',
'Blueberries',
'Pineapples',
'Mangoes',
'Kiwis',
'Watermelons',
];
export default function App() {
const ref = useRef(null);
const [fruits, setFruits] = useState([...allFruits.slice(0, 3)]);
const addFruit = () => {
setFruits((prevFruits) => [...prevFruits, allFruits[prevFruits.length]]);
};
const scrollToLastFruit = () => {
const lastChildElement = ref.current?.lastElementChild;
lastChildElement?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
};
return (
<div>
<div
style={{
position: 'fixed',
backgroundColor: 'white',
bottom: 0,
marginBottom: 10,
}}
>
<button onClick={addFruit}>Add fruit</button>
<button onClick={scrollToLastFruit} style={{ marginLeft: '8px' }}>
Scroll to last
</button>
</div>
<div style={{ height: '5rem' }} />
<div ref={ref}>
{fruits.map((fruit) => (
<h2 key={fruit}>{fruit}</h2>
))}
</div>
<div style={{ height: '150rem' }} />
</div>
);
}
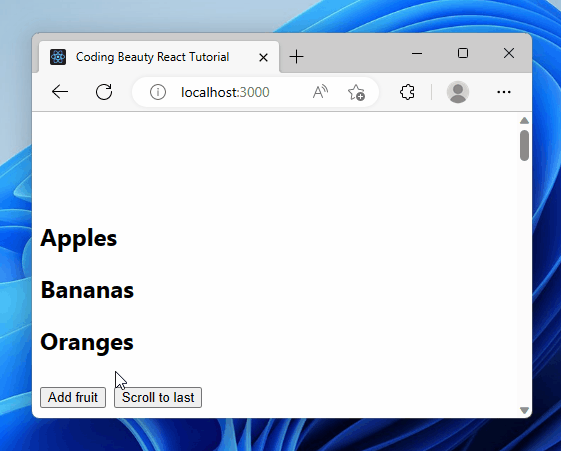
Here we have a list of fruits displayed. The Add fruit button dynamically adds an item to the fruit list on click. Then the Scroll to last button scrolls to this item on click, as it’s the last in the list.
Like before, we use the onClick prop to set a click event listener on the button.
This time we set the ref on the list instead of the items since the items are created dynamically, and the last item will not be constant. Doing this sets the current property of the ref object to the DOM object that represents the list element.
In this listener, we use the lastElementChild property of the list element to get its last item element. Then we call scrollIntoView() on this last item to scroll down to it.
const scrollToLastFruit = () => {
const lastChildElement = ref.current?.lastElementChild;
lastChildElement?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
};Key takeaways
- To scroll to an element after render, set a ref on the element, then call
scrollIntoView()on the ref object inuseEffect. - To scroll to an element on click, set a click listener on the element and call
scrollIntoView()on the ref object in the click event listener. - To scroll to a dynamic element on click, set the ref on the list, use
lastElementChildto get the last item element and callscrollIntoView()on it.
11 Amazing New JavaScript Features in ES13
This guide will bring you up to speed with all the latest features added in ECMAScript 13. These powerful new features will modernize your JavaScript with shorter and more expressive code.