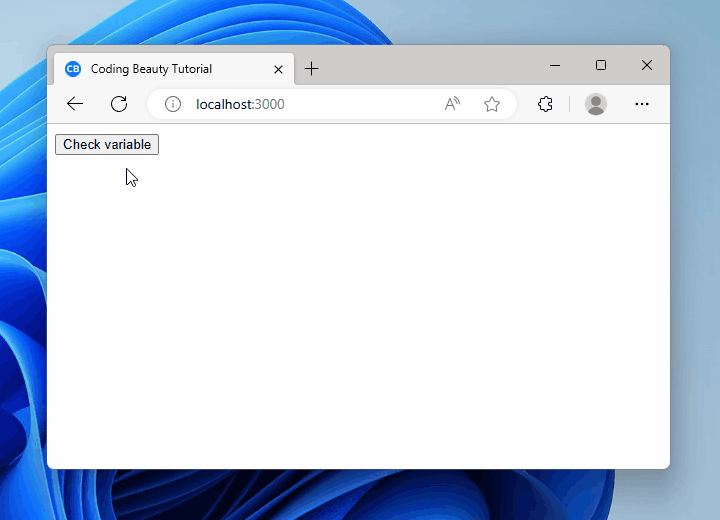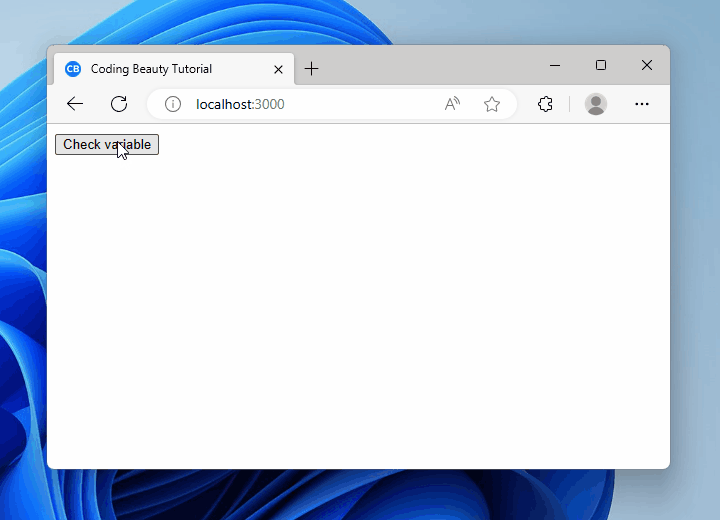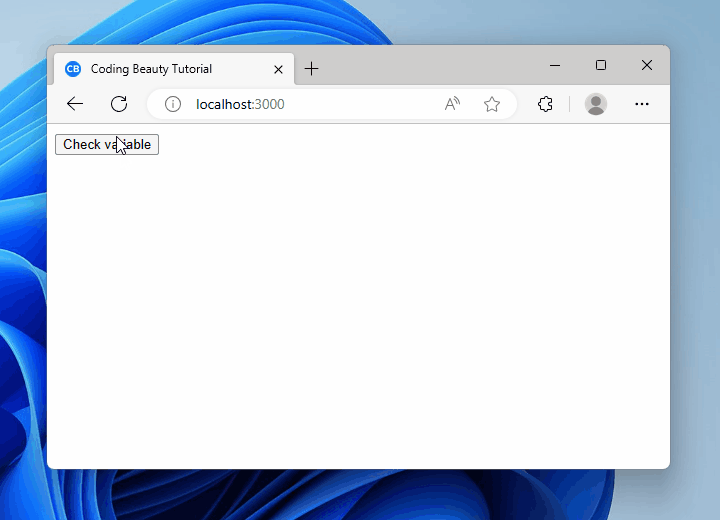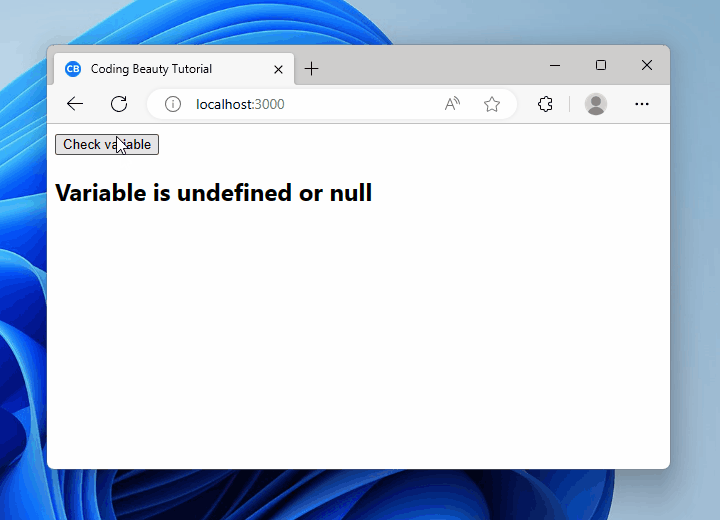
To check if a variable in null or undefined in React, use the || operator to check if the variable is equal to null or equal to undefined.
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function App() {
const [variable] = useState(undefined);
const [message, setMessage] = useState(undefined);
const nullOrUndefinedCheck = () => {
// Check if undefined or null
if (variable === undefined || variable === null) {
setMessage('Variable is undefined or null');
} else {
setMessage('Variable is NOT undefined or null');
}
// Check if NOT undefined or null
if (variable !== undefined && variable !== null) {
setMessage('Variable is NOT undefined or null');
}
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => nullOrUndefinedCheck()}>Check variable</button>
<h2>{message}</h2>
</div>
);
}
The logical OR (||) operator
The logical OR operator (||) results in true if either the value at the left or right is true.
const isTrue = true;
const isFalse = false;
const result1 = isTrue || isFalse;
console.log(result1); // Output: true
const result2 = isFalse || isFalse;
console.log(result2); // Output: falseWhen you use || on non-boolean values, it returns the first truthy value:
const str = '';
const num = 0;
const result1 = str || 'Default String';
console.log(result1); // Output: 'Default String'
const result2 = num || 42;
console.log(result2); // Output: 42The falsy values in JavaScript are undefined, null, 0, NaN, '' (empty string), and false. Every other value is truthy.
Checking if NOT null or undefined with De Morgan’s laws
From De Morgan’s law, not (A or B) = not A and not B, where A and B are boolean conditions.
That’s why we used this condition to check if the variable is not null or undefined:
// not A and not B
if (variable !== undefined && variable !== null) {
setMessage('✅ Variable is NOT undefined or null');
}And why we could just as easily do this:
// not (A or B)
if (!(variable === undefined || variable === null)) {
setMessage('✅ Variable is NOT undefined or null');
}null and undefined are the same with ==
It’s important you use === over == for the check, if you want null and undefined to be treated separately. == is known as the loose equality operator, can you guess why it has that name?
console.log(null == undefined); // true
console.log(null === undefined); // falseLoose equality fails in cases where undefined and null don’t mean the same thing.
Imagine a shopping cart application where a user adds items the cart, represented by a cartItems variable.
- If
cartItemsisundefined, it’ll mean that the shopping cart hasn’t been initialized yet, or an error occurred while fetching it, and we should load this data before proceeding. - If
cartItemsisnull, it’ll mean that the shopping cart is empty – the user hasn’t added any items yet.
Here’s a simplified example of how you might handle this in a React component:
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
const ShoppingCart = () => {
const [cartItems, setCartItems] = useState();
// ...
useEffect(() => {
// Assume fetchCartItems() returns a promise that resolves to the cart items
fetchCartItems()
.then((items) => setCartItems(items))
.catch(() => setCartItems(null));
}, []);
if (cartItems === undefined) {
return <div>Loading cart items...</div>;
} else if (cartItems === null) {
return <div>Your shopping cart is empty! Please add some items.</div>;
} else {
return (
<div>
<h2>Your Shopping Cart</h2>
{cartItems.map((item) => (
<p key={item.id}>{item.name}</p>
))}
</div>
);
}
};
export default ShoppingCart;
If we had used the == operator, only the first comparison to undefined or null would have run.
Check for null, undefined, or anything falsy in React
Instead of checking explicitly for null or undefined, you might be better off checking if the variable is falsy.
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function App() {
const [variable] = useState(undefined);
const [message, setMessage] = useState(undefined);
const falsyCheck = () => {
// Check if falsy
if (!variable) {
setMessage('✅ Variable is falsy');
} else {
setMessage('❌ Variable is NOT falsy');
}
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => falsyCheck()}>Check variable</button>
<h2>{message}</h2>
</div>
);
}By passing the variable to the if statement directly, it is coalesced to a true or false boolean depending on whether the value is truthy or falsy.
The falsy values in JavaScript are undefined, null, 0, NaN, '' (empty string), and false. Every other value is truthy.
11 Amazing New JavaScript Features in ES13
This guide will bring you up to speed with all the latest features added in ECMAScript 13. These powerful new features will modernize your JavaScript with shorter and more expressive code.