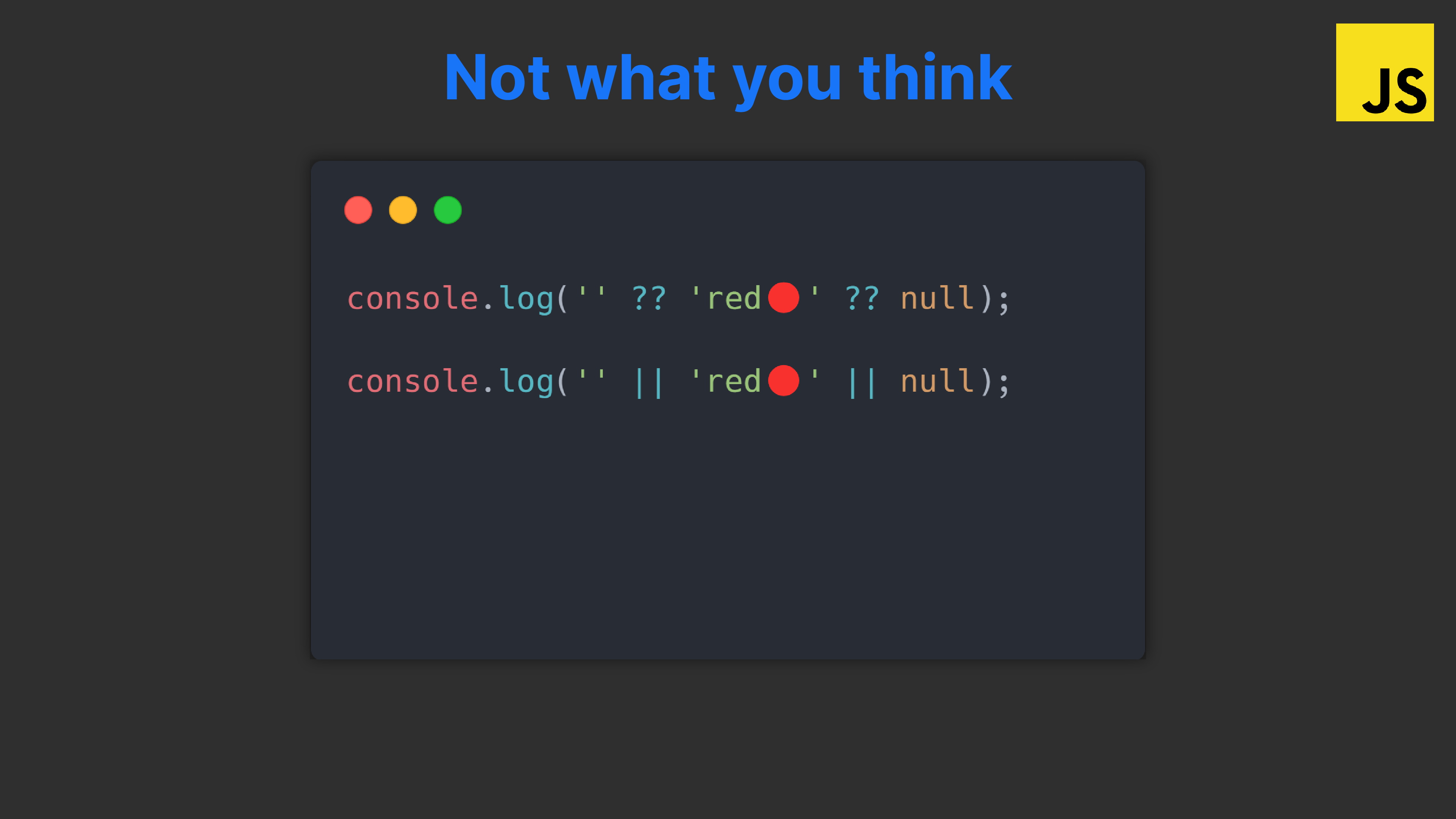
At first glance you think you can just swap in anyone you like right?
let fastest = undefined;
console.log(fastest ?? 'The Flash⚡'); // The Flash⚡
console.log(fastest || 'The Flash⚡'); // The Flash⚡
Wrong. They’re not what you think.
And we must learn the difference once and for all to avoid painful bugs down the line.
And what’s this difference?
It’s the incredible contrast in how they treat truthy and falsy values.
What are these?
Falsy: becomes false in a Boolean() or if:
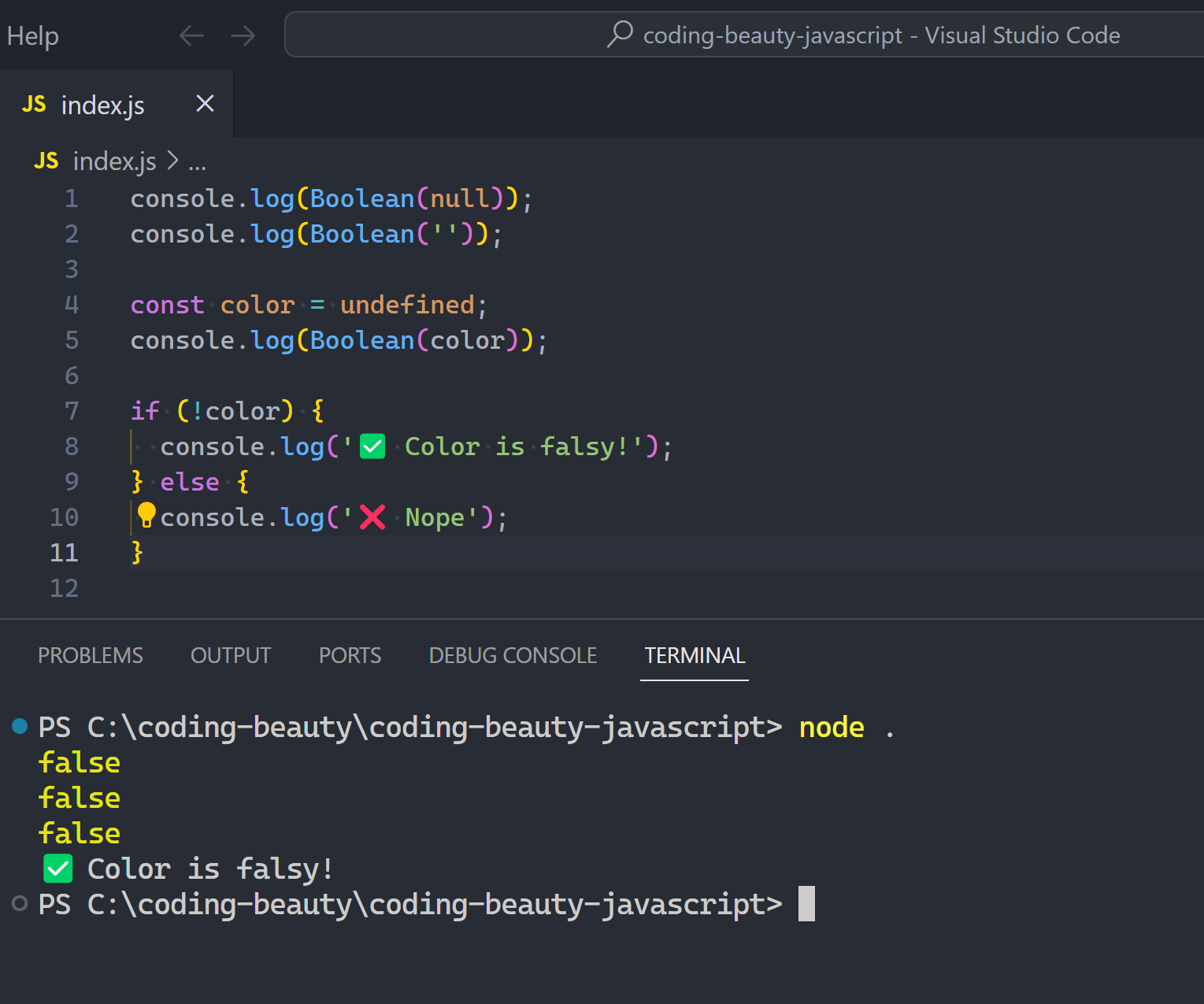
0undefinednullNaNfalse''(empty string)
Truthy: every single thing else:
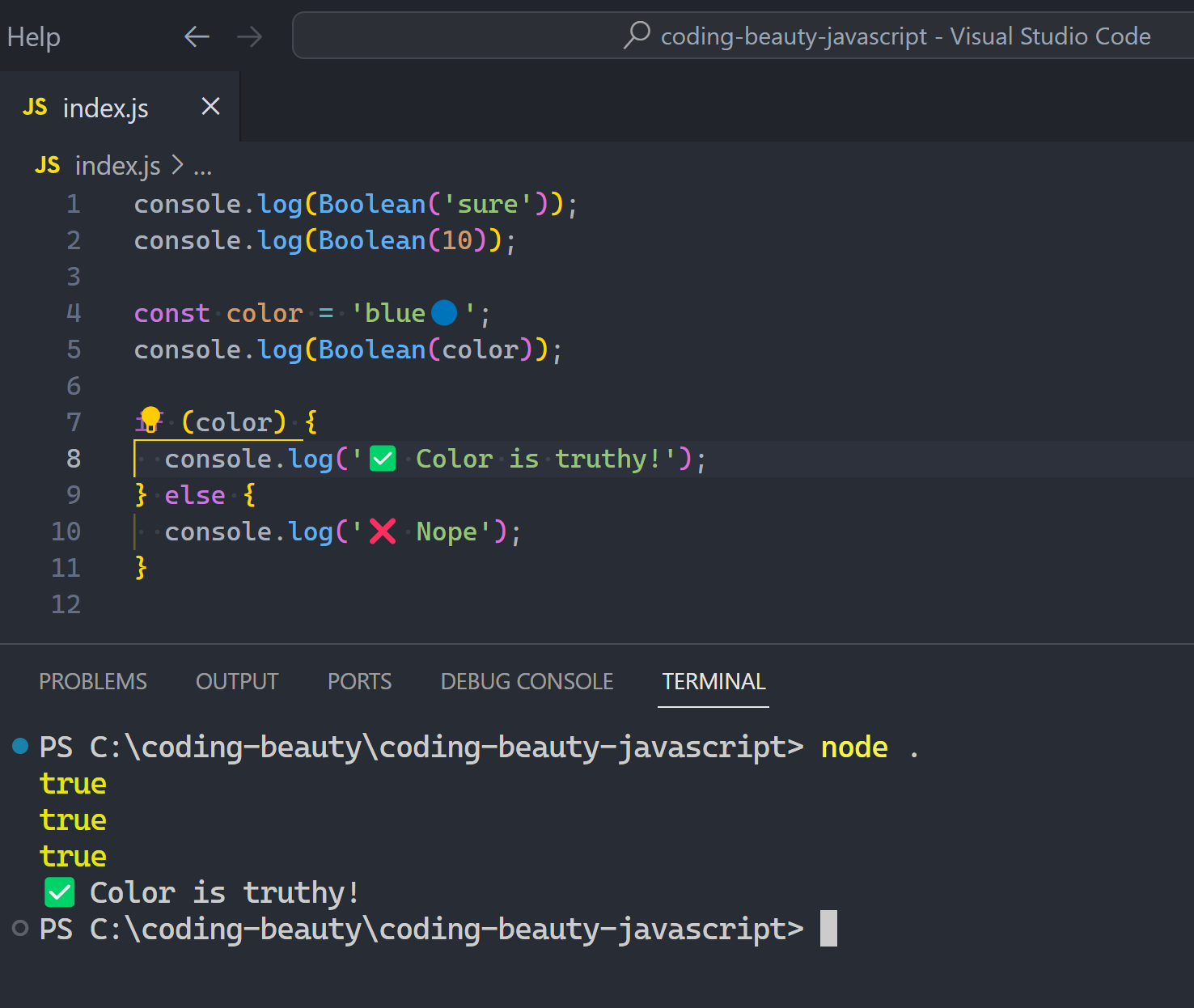
Now see what happens when you create a || chain like this:
const fruit = undefined || null || '' || 'banana🍌';
const color = '' || 'red🔴' || null;
const num = 0 || NaN || 100 || false;
console.log(fruit); // 'banana🍌'
console.log(color); // 'red🔴
console.log(num); // 100
It keeps going until it hits the first truthy!
But what about a ?? chain? 👇
const fruit = undefined ?? null ?? '' ?? 'banana🍌';
const color = '' ?? 'red🔴' ?? null;
const num = 0 ?? NaN ?? 100 ?? false;
console.log(fruit); // '' (empty string)
console.log(color); // ''
console.log(num); // 0Do you see the clear difference?
One looks for truthy, the other looks for anything that isn’t null or undefined.
When to use ?? vs ||
Initializing extra lives in a video game, where 0 means something?
?? 👇
const data = loadData();
const player = initPlayer(data);
function initPlayer({ extraLives }) {
const extraLives = extraLives ?? 20;
console.log(`Player extra lives: ${extraLives}`);
}Paginating a response, where 0 limit makes no sense?
|| 👇
function paginate(options = {}) {
return ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'].splice(0, options.limit || 3);
}
paginate(1); // Output: ['a']
paginate(); // Output: ['a', 'b', 'c']
paginate(0); // Output: ['a', 'b', 'c']User must have a name, so no spaces and definitely no empty strings?
|| 👇
function getUsername(userInput) {
return userInput || 'Guest';
}
function getProfilePic(userInput) {
return userInput || 'profile-pic.png';
}Did the user enter an invalid number or did they enter a number at all?
Find out with ?? 👇
function getUserAge(input) {
if (!input) {
return null;
} else {
return Number(input);
}
}
console.log(getUserAge('') ?? '❌');
console.log(getUserAge('314') ?? '❌');
console.log(getUserAge('green🟢') ?? '❌');
?? and ?. are friends
Is someone there? not null or undefined?
Yes:
??— alright I’m done here?.— So let’s check out what you’ve gone
No:
??— So who’s next??.— Um… bye!
console.log(''?.length); // 0
console.log('' ?? '❌'); // ''
console.log('Tari Ibaba'?.length); // 10
console.log('Tari Ibaba' ?? '❌'); // 'Tari Ibaba'
console.log(null?.length); // undefined
console.log(null ?? '❌'); // '❌'
console.log(undefined?.length); // undefined
console.log(undefined ?? '❌'); // '❌'
Final thoughts
?? is a gullible child who will believe anything.
|| is a detective in search of the truthy and nothing but the truthy.
Every Crazy Thing JavaScript Does
A captivating guide to the subtle caveats and lesser-known parts of JavaScript.