JavaScript has no native event for listening for URL changes in the browser, so to do this, you can create an interval listener that compares the current URL value to the previous value every X seconds.
let prevUrl = undefined;
setInterval(() => {
const currUrl = window.location.href;
if (currUrl != prevUrl) {
// URL changed
prevUrl = currUrl;
console.log(`URL changed to : ${currUrl}`);
}
}, 60);
We call setInterval() with a callback and 60 to invoke the callback every 60 seconds. In the callback, we check if the current URL is the same as the last URL; if it is, we perform our desired action.
For example:
<button id="change-url">Change URL</button>
<br /><br />
<span id="url-change-indicator"></span>#url-change-indicator {
white-space: pre;
}const urlChangeIndicator = document.getElementById('url-change-indicator');
let prevUrl = undefined;
setInterval(() => {
const currUrl = window.location.href;
if (currUrl != prevUrl) {
// URL changed
prevUrl = currUrl;
console.log(`URL changed to: ${currUrl}`);
urlChangeIndicator.textContent += `New URL: ${currUrl}\r\n`;
}
}, 60);
const changeUrl = document.getElementById('change-url');
changeUrl.addEventListener('click', () => {
history.pushState({}, '', 'new-page.html');
});
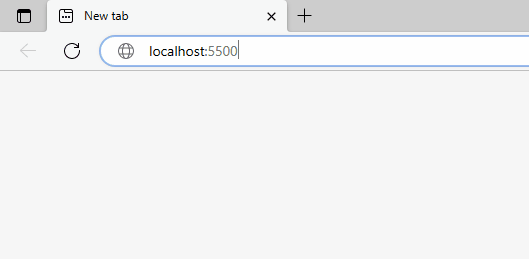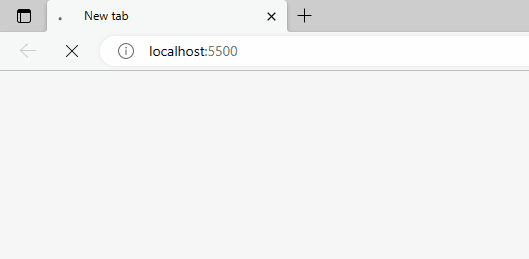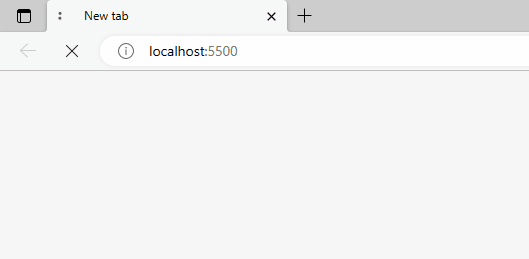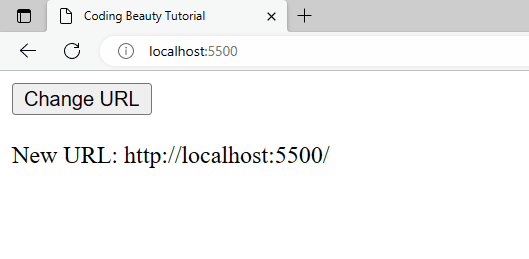
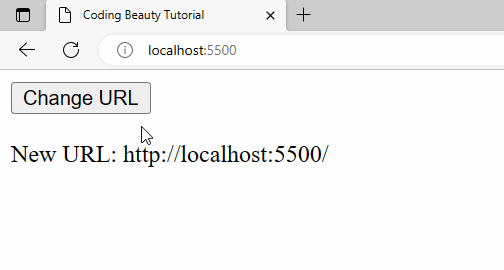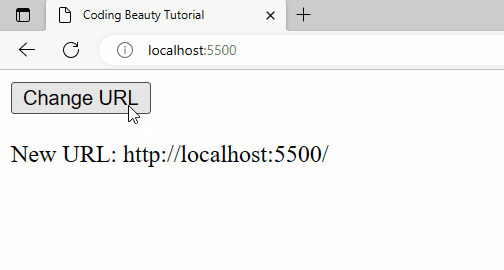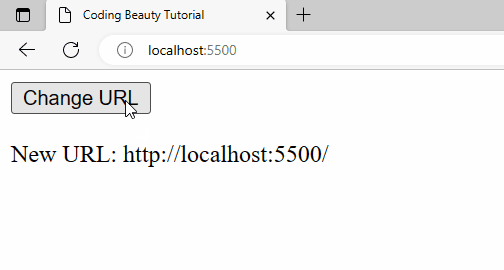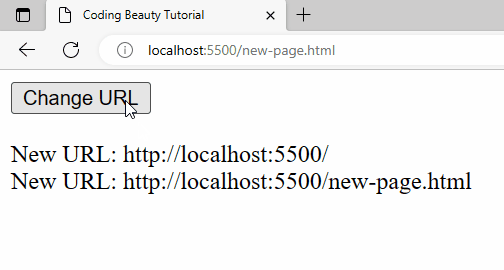
A URL change is detected right away when the page is first loaded:
A URL change will also be detected when history.pushState() is called from the Change URL button’s click event listener.
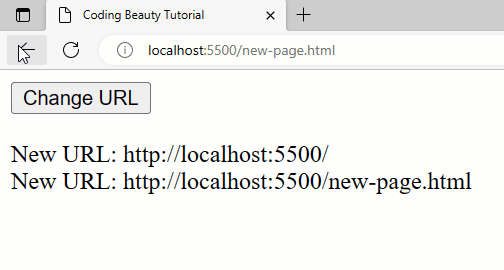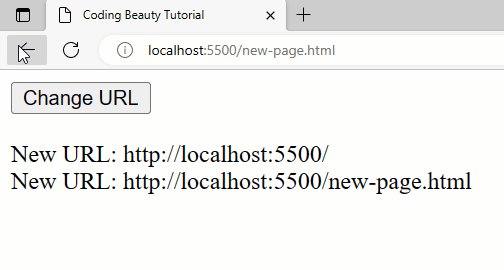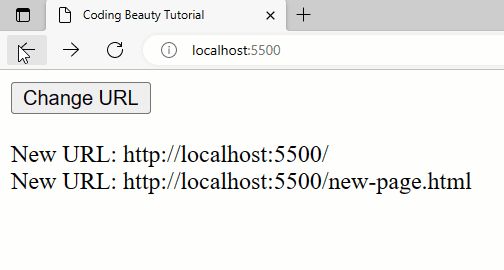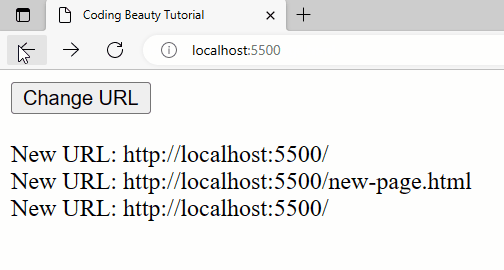
Detect back button click
Apart from pushState(), this approach will also work when the back button is clicked, whether by the user or with a method like history.back().
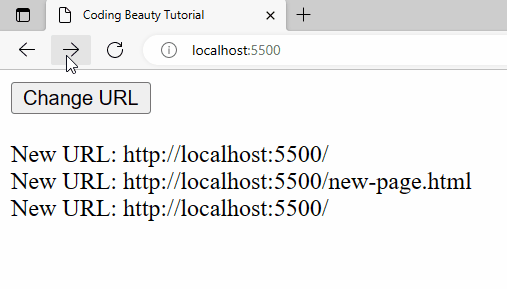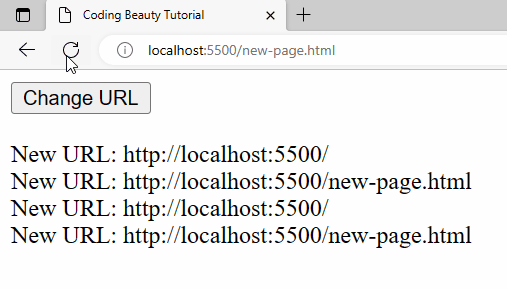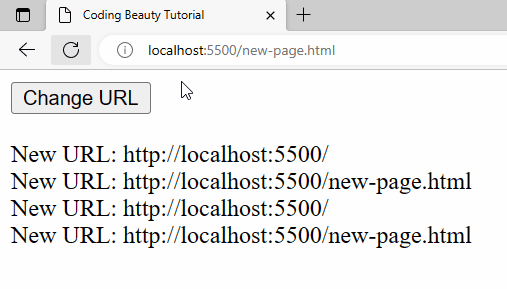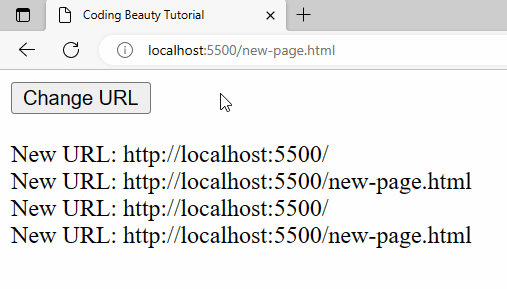
Detect forward button click
The same thing applies to a forward button click or history.forward():
Use detect-url-change library
Alternatively, you can use the detect-url-change library to quickly change the browser URL.
import detectChangeUrl from 'detect-url-change';
detectChangeUrl.on('change', (newUrl) => {
console.log(`URL changed to ${newUrl}`);
});The default export is an observer on which you can attach listeners to perform an action when the URL changes.
For example:
<button id="change-url">Change URL</button>
<br /><br />
<span id="url-change-indicator"></span>#url-change-indicator {
white-space: pre;
}
* {
font-family: 'Segoe UI';
}import detectChangeUrl from 'detect-url-change';
const urlChangeIndicator = document.querySelector('#url-change-indicator');
detectChangeUrl.on('change', (newUrl) => {
console.log(`URL changed to ${newUrl}`);
urlChangeIndicator.textContent += `New URL: ${newUrl}\r\n`;
});
const changeUrl = document.getElementById('change-url');
changeUrl.addEventListener('click', () => {
history.pushState({}, '', 'new-page.html');
});
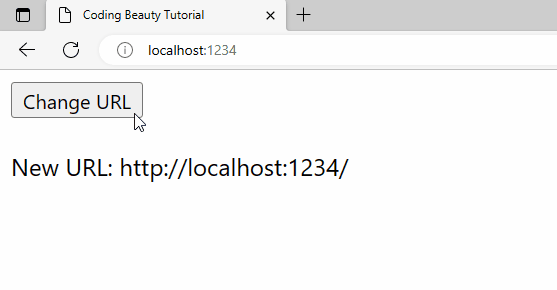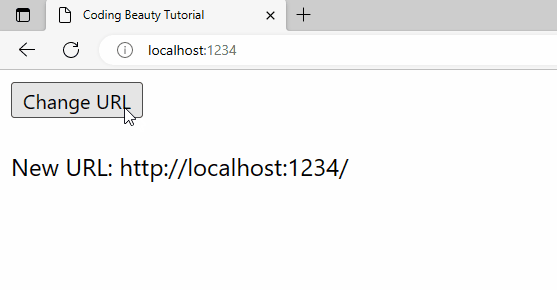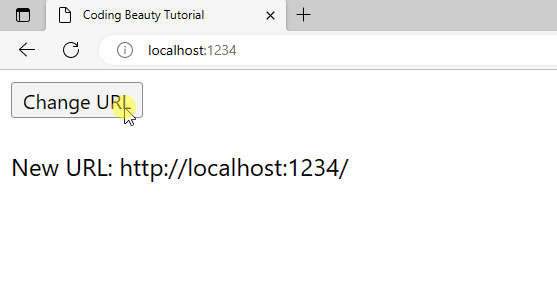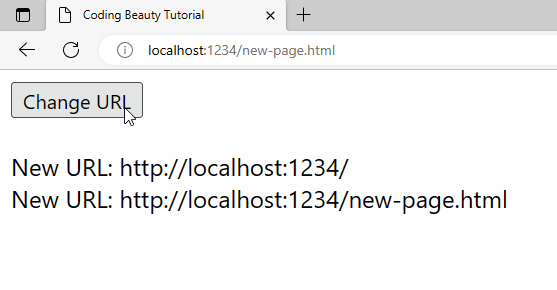
pushState() call in the button’s click event listener.To use detect-url-change like in this example, you’ll first need to install it into your project. You can do this with the following command:
npm i detect-url-change
# Yarn
yarn add detect-url-changeYou’ll also need to use a bundling tool like Webpack, Rollup, Parcel, etc.
Every Crazy Thing JavaScript Does
A captivating guide to the subtle caveats and lesser-known parts of JavaScript.